Oversamplers
NoSMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.NoSMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
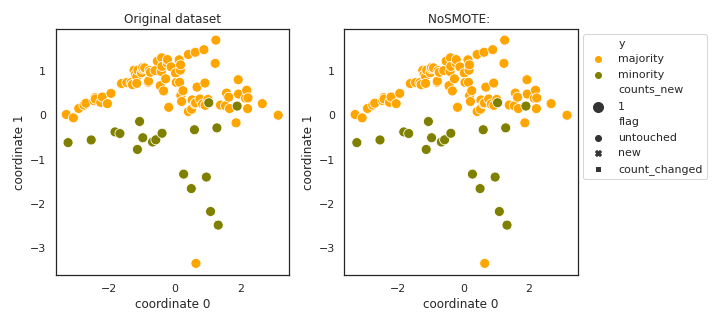
The goal of this class is to provide a functionality to send data through on any model selection/evaluation pipeline with no oversampling carried out. It can be used to get baseline estimates on preformance.
SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
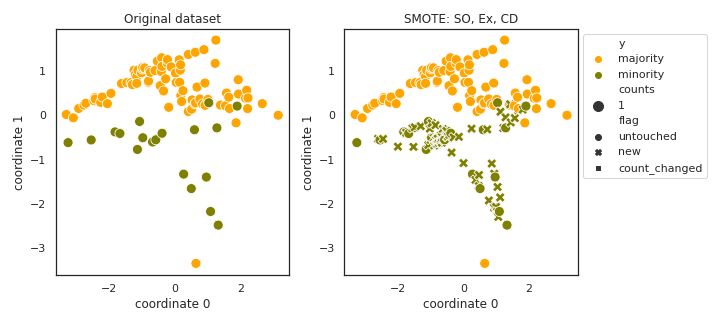
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote, author={Chawla, N. V. and Bowyer, K. W. and Hall, L. O. and Kegelmeyer, W. P.}, title={{SMOTE}: synthetic minority over-sampling technique}, journal={Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research}, volume={16}, year={2002}, pages={321--357} }
SMOTE_TomekLinks
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_TomekLinks()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
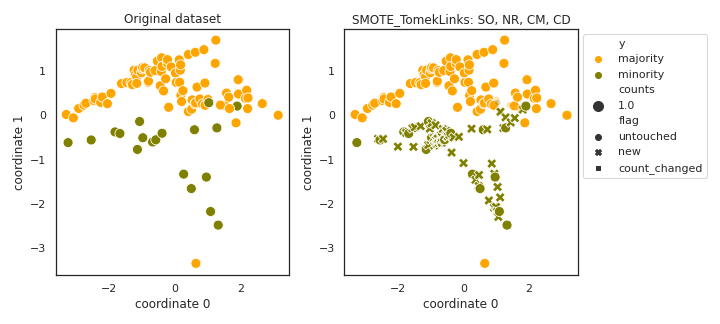
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_tomeklinks_enn, author = {Batista, Gustavo E. A. P. A. and Prati, Ronaldo C. and Monard, Maria Carolina}, title = {A Study of the Behavior of Several Methods for Balancing Machine Learning Training Data}, journal = {SIGKDD Explor. Newsl.}, issue_date = {June 2004}, volume = {6}, number = {1}, month = jun, year = {2004}, issn = {1931-0145}, pages = {20--29}, numpages = {10}, url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1007730.1007735}, doi = {10.1145/1007730.1007735}, acmid = {1007735}, publisher = {ACM}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, }
SMOTE_ENN
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_ENN()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
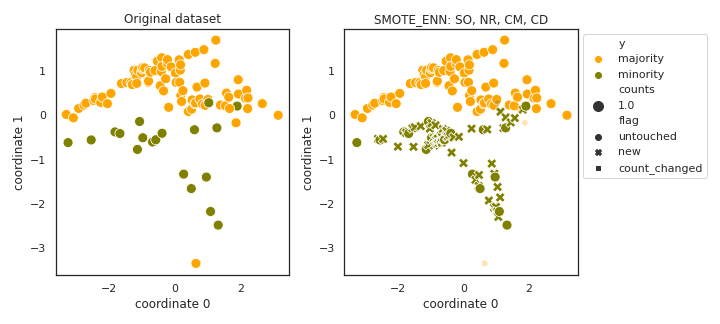
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_tomeklinks_enn, author = {Batista, Gustavo E. A. P. A. and Prati, Ronaldo C. and Monard, Maria Carolina}, title = {A Study of the Behavior of Several Methods for Balancing Machine Learning Training Data}, journal = {SIGKDD Explor. Newsl.}, issue_date = {June 2004}, volume = {6}, number = {1}, month = jun, year = {2004}, issn = {1931-0145}, pages = {20--29}, numpages = {10}, url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1007730.1007735}, doi = {10.1145/1007730.1007735}, acmid = {1007735}, publisher = {ACM}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, }
- Notes:
Can remove too many of minority samples.
Borderline_SMOTE1
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Borderline_SMOTE1()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
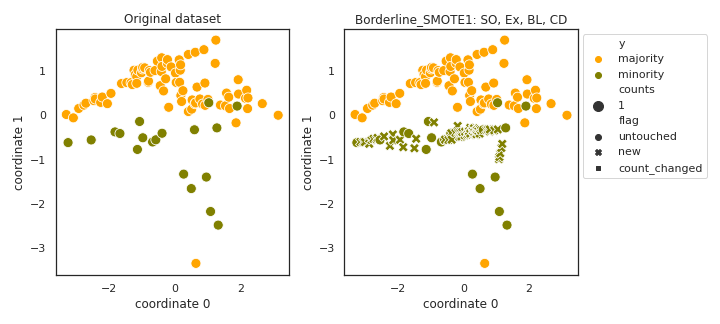
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{borderlineSMOTE, author="Han, Hui and Wang, Wen-Yuan and Mao, Bing-Huan", editor="Huang, De-Shuang and Zhang, Xiao-Ping and Huang, Guang-Bin", title="Borderline-SMOTE: A New Over-Sampling Method in Imbalanced Data Sets Learning", booktitle="Advances in Intelligent Computing", year="2005", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="878--887", isbn="978-3-540-31902-3" }
Borderline_SMOTE2
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Borderline_SMOTE2()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
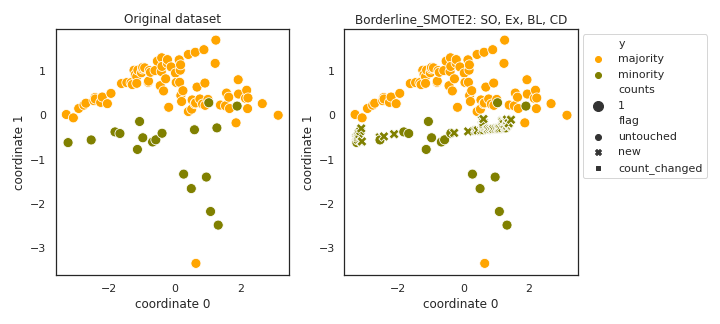
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{borderlineSMOTE, author="Han, Hui and Wang, Wen-Yuan and Mao, Bing-Huan", editor="Huang, De-Shuang and Zhang, Xiao-Ping and Huang, Guang-Bin", title="Borderline-SMOTE: A New Over-Sampling Method in Imbalanced Data Sets Learning", booktitle="Advances in Intelligent Computing", year="2005", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="878--887", isbn="978-3-540-31902-3" }
ADASYN
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ADASYN()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
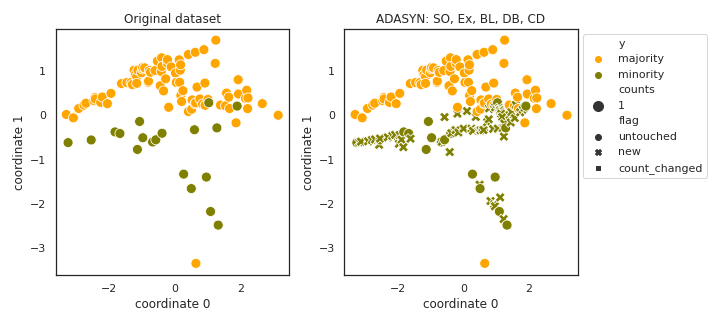
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{adasyn, author={He, H. and Bai, Y. and Garcia, E. A. and Li, S.}, title={{ADASYN}: adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning}, booktitle={Proceedings of IJCNN}, year={2008}, pages={1322--1328} }
AHC
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.AHC()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
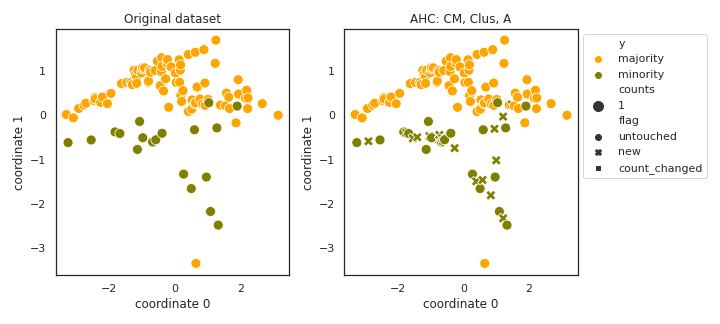
- References:
BibTex:
@article{AHC, title = "Learning from imbalanced data in surveillance of nosocomial infection", journal = "Artificial Intelligence in Medicine", volume = "37", number = "1", pages = "7 - 18", year = "2006", note = "Intelligent Data Analysis in Medicine", issn = "0933-3657", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2005.03.002", url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/ pii/S0933365705000850}, author = "Gilles Cohen and Mélanie Hilario and Hugo Sax and Stéphane Hugonnet and Antoine Geissbuhler", keywords = "Nosocomial infection, Machine learning, Support vector machines, Data imbalance" }
LLE_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.LLE_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
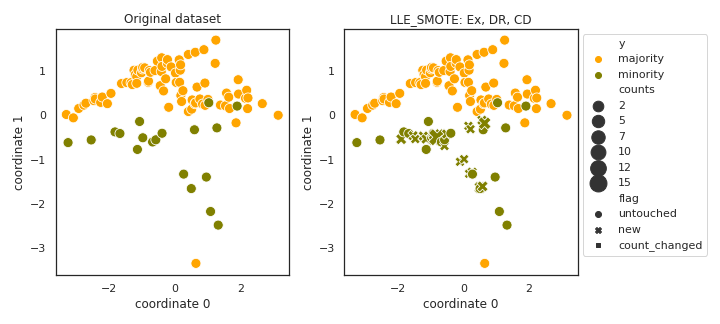
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{lle_smote, author={Wang, J. and Xu, M. and Wang, H. and Zhang, J.}, booktitle={2006 8th international Conference on Signal Processing}, title={Classification of Imbalanced Data by Using the SMOTE Algorithm and Locally Linear Embedding}, year={2006}, volume={3}, number={}, pages={}, keywords={artificial intelligence; biomedical imaging;medical computing; imbalanced data classification; SMOTE algorithm; locally linear embedding; medical imaging intelligence; synthetic minority oversampling technique; high-dimensional data; low-dimensional space; Biomedical imaging; Back;Training data; Data mining;Biomedical engineering; Research and development; Electronic mail;Pattern recognition; Performance analysis; Classification algorithms}, doi={10.1109/ICOSP.2006.345752}, ISSN={2164-5221}, month={Nov}}
- Notes:
- There might be numerical issues if the nearest neighbors contain
some element multiple times.
distance_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.distance_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
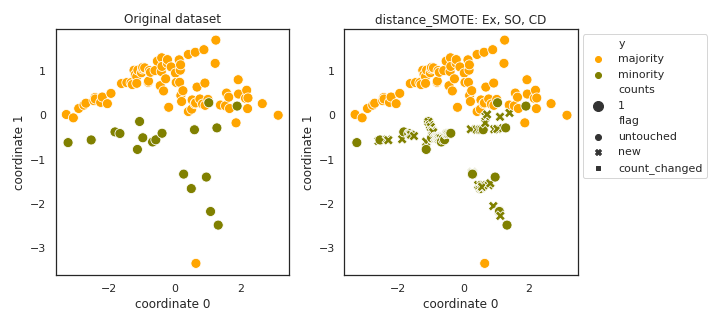
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{distance_smote, author={de la Calleja, J. and Fuentes, O.}, booktitle={Proceedings of the Twentieth International Florida Artificial Intelligence}, title={A distance-based over-sampling method for learning from imbalanced data sets}, year={2007}, volume={3}, pages={634--635} }
- Notes:
It is not clear what the authors mean by “weighted distance”.
SMMO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMMO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
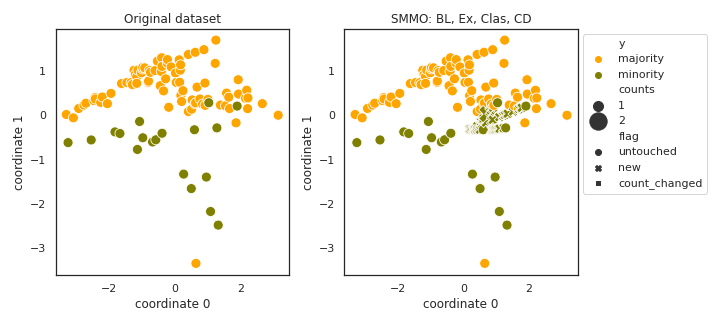
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{smmo, author = {de la Calleja, Jorge and Fuentes, Olac and González, Jesús}, booktitle= {Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference}, year = {2008}, month = {01}, pages = {276-281}, title = {Selecting Minority Examples from Misclassified Data for Over-Sampling.} }
- Notes:
- In this paper the ensemble is not specified. I have selected
some very fast, basic classifiers.
Also, it is not clear what the authors mean by “weighted distance”.
- The original technique is not prepared for the case when no minority
samples are classified correctly be the ensemble.
polynom_fit_SMOTE_bus
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.polynom_fit_SMOTE_bus()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
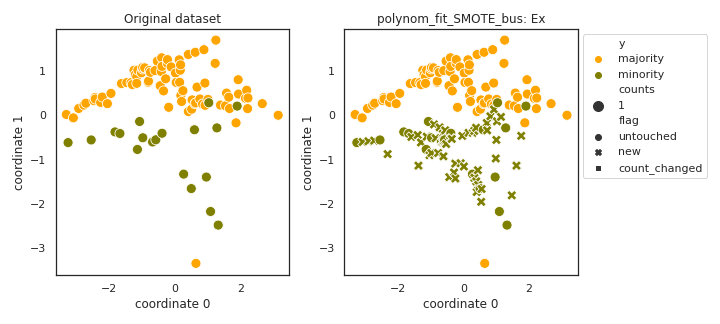
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{polynomial_fit_smote, author={Gazzah, S. and Amara, N. E. B.}, booktitle={2008 The Eighth IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems}, title={New Oversampling Approaches Based on Polynomial Fitting for Imbalanced Data Sets}, year={2008}, volume={}, number={}, pages={677-684}, keywords={curve fitting;learning (artificial intelligence);mesh generation;pattern classification;polynomials;sampling methods;support vector machines; oversampling approach;polynomial fitting function;imbalanced data set;pattern classification task; class-modular strategy;support vector machine;true negative rate; true positive rate;star topology; bus topology;polynomial curve topology;mesh topology;Polynomials; Topology;Support vector machines; Support vector machine classification; Pattern classification;Performance evaluation;Training data;Text analysis;Data engineering;Convergence; writer identification system;majority class;minority class;imbalanced data sets;polynomial fitting functions; class-modular strategy}, doi={10.1109/DAS.2008.74}, ISSN={}, month={Sept},}
polynom_fit_SMOTE_mesh
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.polynom_fit_SMOTE_mesh()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
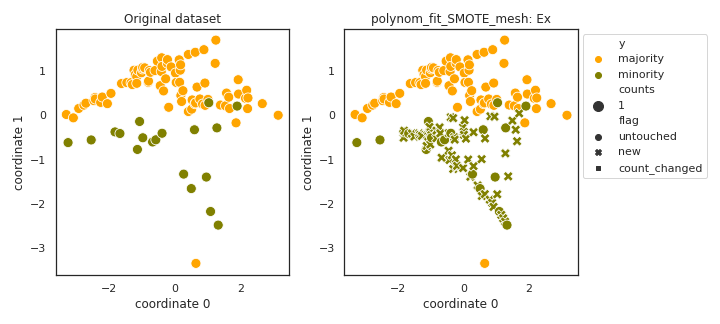
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{polynomial_fit_smote, author={Gazzah, S. and Amara, N. E. B.}, booktitle={2008 The Eighth IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems}, title={New Oversampling Approaches Based on Polynomial Fitting for Imbalanced Data Sets}, year={2008}, volume={}, number={}, pages={677-684}, keywords={curve fitting;learning (artificial intelligence);mesh generation;pattern classification;polynomials;sampling methods;support vector machines; oversampling approach;polynomial fitting function;imbalanced data set;pattern classification task; class-modular strategy;support vector machine;true negative rate; true positive rate;star topology; bus topology;polynomial curve topology;mesh topology;Polynomials; Topology;Support vector machines; Support vector machine classification; Pattern classification;Performance evaluation;Training data;Text analysis;Data engineering;Convergence; writer identification system;majority class;minority class;imbalanced data sets;polynomial fitting functions; class-modular strategy}, doi={10.1109/DAS.2008.74}, ISSN={}, month={Sept},}
polynom_fit_SMOTE_star
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.polynom_fit_SMOTE_star()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
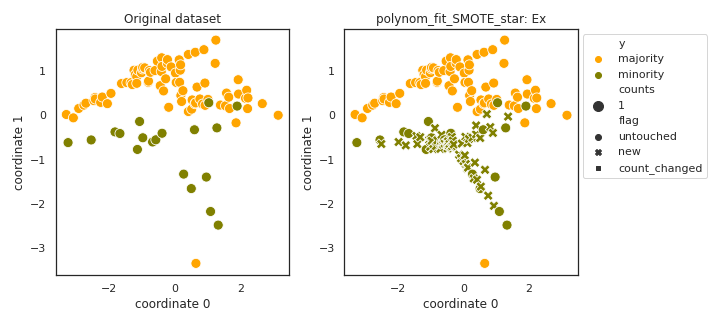
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{polynomial_fit_smote, author={Gazzah, S. and Amara, N. E. B.}, booktitle={2008 The Eighth IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems}, title={New Oversampling Approaches Based on Polynomial Fitting for Imbalanced Data Sets}, year={2008}, volume={}, number={}, pages={677-684}, keywords={curve fitting;learning (artificial intelligence);mesh generation;pattern classification;polynomials;sampling methods;support vector machines; oversampling approach;polynomial fitting function;imbalanced data set;pattern classification task; class-modular strategy;support vector machine;true negative rate; true positive rate;star topology; bus topology;polynomial curve topology;mesh topology;Polynomials; Topology;Support vector machines; Support vector machine classification; Pattern classification;Performance evaluation;Training data;Text analysis;Data engineering;Convergence; writer identification system;majority class;minority class;imbalanced data sets;polynomial fitting functions; class-modular strategy}, doi={10.1109/DAS.2008.74}, ISSN={}, month={Sept},}
polynom_fit_SMOTE_poly
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.polynom_fit_SMOTE_poly()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
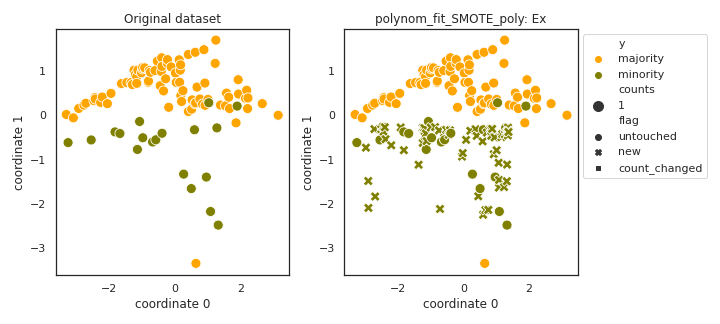
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{polynomial_fit_smote, author={Gazzah, S. and Amara, N. E. B.}, booktitle={2008 The Eighth IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems}, title={New Oversampling Approaches Based on Polynomial Fitting for Imbalanced Data Sets}, year={2008}, volume={}, number={}, pages={677-684}, keywords={curve fitting;learning (artificial intelligence);mesh generation;pattern classification;polynomials;sampling methods;support vector machines; oversampling approach;polynomial fitting function;imbalanced data set;pattern classification task; class-modular strategy;support vector machine;true negative rate; true positive rate;star topology; bus topology;polynomial curve topology;mesh topology;Polynomials; Topology;Support vector machines; Support vector machine classification; Pattern classification;Performance evaluation;Training data;Text analysis;Data engineering;Convergence; writer identification system;majority class;minority class;imbalanced data sets;polynomial fitting functions; class-modular strategy}, doi={10.1109/DAS.2008.74}, ISSN={}, month={Sept},}
Stefanowski
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Stefanowski()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
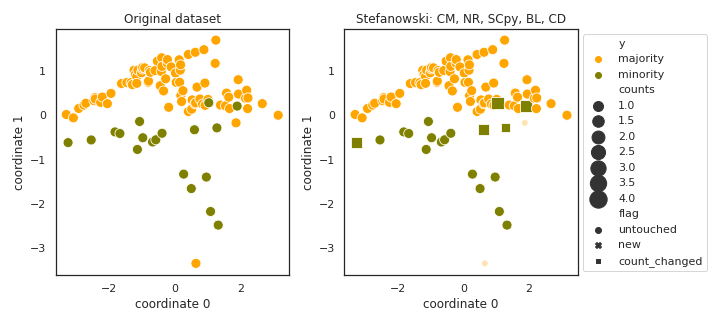
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{stefanowski, author = {Stefanowski, Jerzy and Wilk, Szymon}, title = {Selective Pre-processing of Imbalanced Data for Improving Classification Performance}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Data Warehousing and Knowledge Discovery}, series = {DaWaK '08}, year = {2008}, isbn = {978-3-540-85835-5}, location = {Turin, Italy}, pages = {283--292}, numpages = {10}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85836-2_27}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-540-85836-2_27}, acmid = {1430591}, publisher = {Springer-Verlag}, address = {Berlin, Heidelberg}, }
Safe_Level_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Safe_Level_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
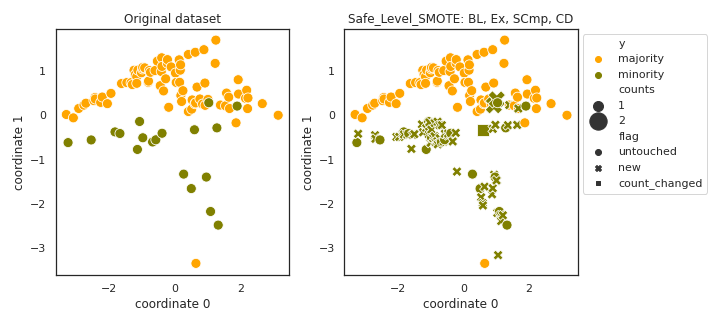
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{safe_level_smote, author = { Bunkhumpornpat, Chumphol and Sinapiromsaran, Krung and Lursinsap, Chidchanok}, title = {Safe-Level-SMOTE: Safe-Level-Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling TEchnique for Handling the Class Imbalanced Problem}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 13th Pacific-Asia Conference on Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining}, series = {PAKDD '09}, year = {2009}, isbn = {978-3-642-01306-5}, location = {Bangkok, Thailand}, pages = {475--482}, numpages = {8}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01307-2_43}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-01307-2_43}, acmid = {1533904}, publisher = {Springer-Verlag}, address = {Berlin, Heidelberg}, keywords = {Class Imbalanced Problem, Over-sampling, SMOTE, Safe Level}, }
- Notes:
- The original method was not prepared for the case when no minority
sample has minority neighbors.
MSMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.MSMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
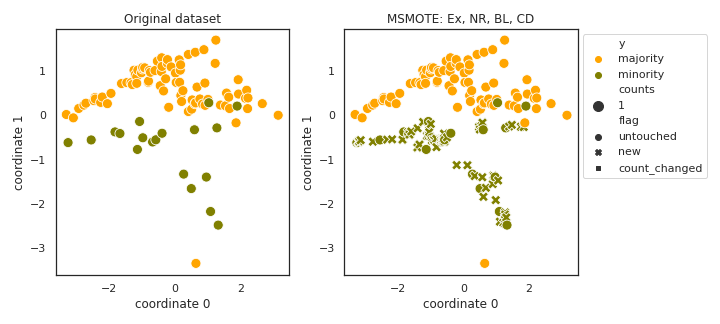
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{msmote, author = {Hu, Shengguo and Liang, Yanfeng and Ma, Lintao and He, Ying}, title = {MSMOTE: Improving Classification Performance When Training Data is Imbalanced}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2009 Second International Workshop on Computer Science and Engineering - Volume 02}, series = {IWCSE '09}, year = {2009}, isbn = {978-0-7695-3881-5}, pages = {13--17}, numpages = {5}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/WCSE.2009.756}, doi = {10.1109/WCSE.2009.756}, acmid = {1682710}, publisher = {IEEE Computer Society}, address = {Washington, DC, USA}, keywords = {imbalanced data, over-sampling, SMOTE, AdaBoost, samples groups, SMOTEBoost}, }
- Notes:
- The original method was not prepared for the case when all
minority samples are noise.
DE_oversampling
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.DE_oversampling()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
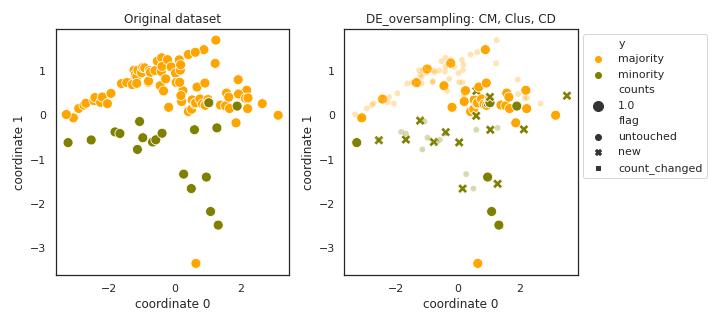
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{de_oversampling, author={Chen, L. and Cai, Z. and Chen, L. and Gu, Q.}, booktitle={2010 Third International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining}, title={A Novel Differential Evolution-Clustering Hybrid Resampling Algorithm on Imbalanced Datasets}, year={2010}, volume={}, number={}, pages={81-85}, keywords={pattern clustering;sampling methods; support vector machines;differential evolution;clustering algorithm;hybrid resampling algorithm;imbalanced datasets;support vector machine; minority class;mutation operators; crossover operators;data cleaning method;F-measure criterion;ROC area criterion;Support vector machines; Intrusion detection;Support vector machine classification;Cleaning; Electronic mail;Clustering algorithms; Signal to noise ratio;Learning systems;Data mining;Geology;imbalanced datasets;hybrid resampling;clustering; differential evolution;support vector machine}, doi={10.1109/WKDD.2010.48}, ISSN={}, month={Jan},}
SMOBD
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOBD()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
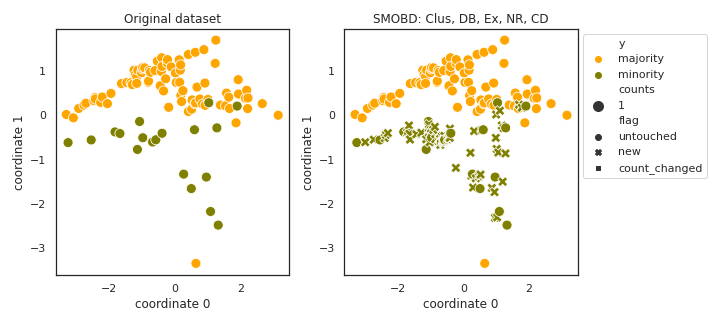
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{smobd, author={Cao, Q. and Wang, S.}, booktitle={2011 International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering}, title={Applying Over-sampling Technique Based on Data Density and Cost-sensitive SVM to Imbalanced Learning}, year={2011}, volume={2}, number={}, pages={543-548}, keywords={data handling;learning (artificial intelligence);support vector machines; oversampling technique application; data density;cost sensitive SVM; imbalanced learning;SMOTE algorithm; data distribution;density information; Support vector machines;Classification algorithms;Noise measurement;Arrays; Noise;Algorithm design and analysis; Training;imbalanced learning; cost-sensitive SVM;SMOTE;data density; SMOBD}, doi={10.1109/ICIII.2011.276}, ISSN={2155-1456}, month={Nov},}
SUNDO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SUNDO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
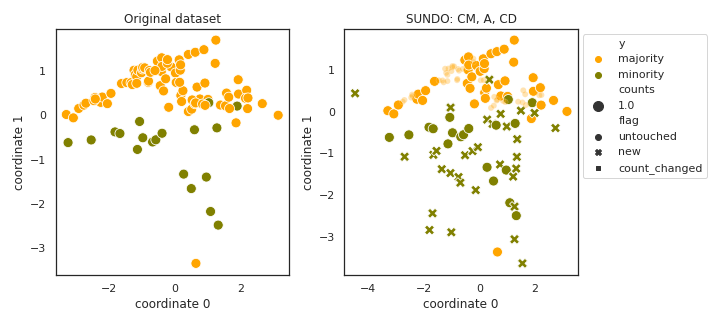
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{sundo, author={Cateni, S. and Colla, V. and Vannucci, M.}, booktitle={2011 11th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications}, title={Novel resampling method for the classification of imbalanced datasets for industrial and other real-world problems}, year={2011}, volume={}, number={}, pages={402-407}, keywords={decision trees;pattern classification; sampling methods;support vector machines;resampling method;imbalanced dataset classification;industrial problem;real world problem; oversampling technique;undersampling technique;support vector machine; decision tree;binary classification; synthetic dataset;public dataset; industrial dataset;Support vector machines;Training;Accuracy;Databases; Intelligent systems;Breast cancer; Decision trees;oversampling; undersampling;imbalanced dataset}, doi={10.1109/ISDA.2011.6121689}, ISSN={2164-7151}, month={Nov}}
MSYN
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.MSYN()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
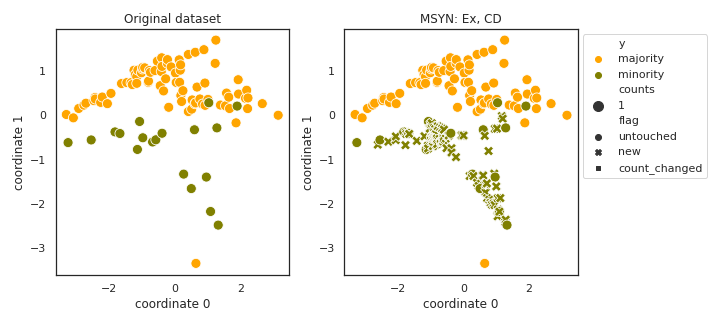
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{msyn, author="Fan, Xiannian and Tang, Ke and Weise, Thomas", editor="Huang, Joshua Zhexue and Cao, Longbing and Srivastava, Jaideep", title="Margin-Based Over-Sampling Method for Learning from Imbalanced Datasets", booktitle="Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining", year="2011", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="309--320", abstract="Learning from imbalanced datasets has drawn more and more attentions from both theoretical and practical aspects. Over- sampling is a popular and simple method for imbalanced learning. In this paper, we show that there is an inherently potential risk associated with the over-sampling algorithms in terms of the large margin principle. Then we propose a new synthetic over sampling method, named Margin-guided Synthetic Over-sampling (MSYN), to reduce this risk. The MSYN improves learning with respect to the data distributions guided by the margin-based rule. Empirical study verities the efficacy of MSYN.", isbn="978-3-642-20847-8" }
SVM_balance
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SVM_balance()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
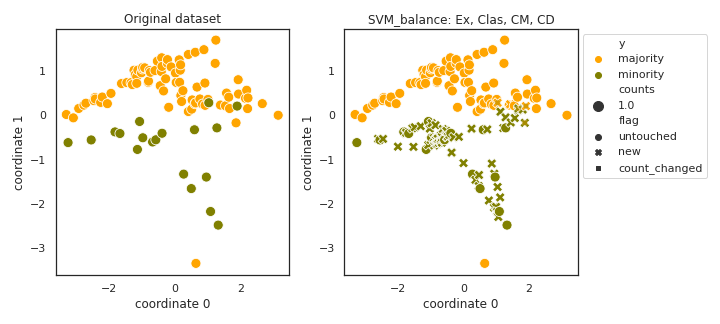
- References:
BibTex:
@article{svm_balance, author = {Farquad, M.A.H. and Bose, Indranil}, title = {Preprocessing Unbalanced Data Using Support Vector Machine}, journal = {Decis. Support Syst.}, issue_date = {April, 2012}, volume = {53}, number = {1}, month = apr, year = {2012}, issn = {0167-9236}, pages = {226--233}, numpages = {8}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.01.016}, doi = {10.1016/j.dss.2012.01.016}, acmid = {2181554}, publisher = {Elsevier Science Publishers B. V.}, address = {Amsterdam, The Netherlands, The Netherlands}, keywords = {COIL data, Hybrid method, Preprocessor, SVM, Unbalanced data}, }
TRIM_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.TRIM_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
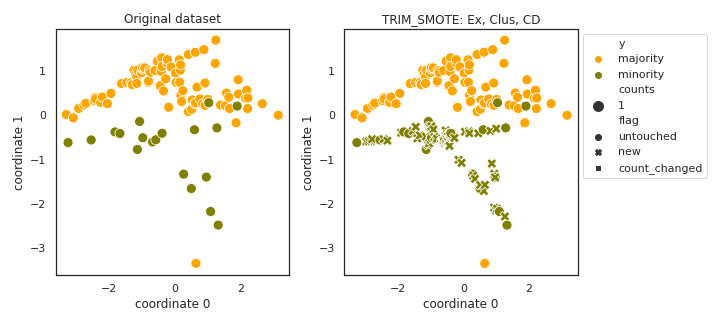
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{trim_smote, author="Puntumapon, Kamthorn and Waiyamai, Kitsana", editor="Tan, Pang-Ning and Chawla, Sanjay and Ho, Chin Kuan and Bailey, James", title="A Pruning-Based Approach for Searching Precise and Generalized Region for Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling", booktitle="Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining", year="2012", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="371--382", isbn="978-3-642-30220-6" }
- Notes:
- It is not described precisely how the filtered data is used for
sample generation. The method is proposed to be a preprocessing step, and it states that it applies sample generation to each group extracted.
SMOTE_RSB
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_RSB()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
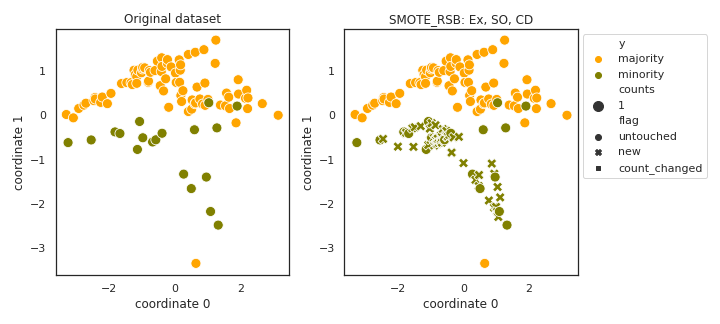
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{smote_rsb, author="Ramentol, Enislay and Caballero, Yail{'e} and Bello, Rafael and Herrera, Francisco", title="SMOTE-RSB*: a hybrid preprocessing approach based on oversampling and undersampling for high imbalanced data-sets using SMOTE and rough sets theory", journal="Knowledge and Information Systems", year="2012", month="Nov", day="01", volume="33", number="2", pages="245--265", issn="0219-3116", doi="10.1007/s10115-011-0465-6", url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-011-0465-6" }
- Notes:
- I think the description of the algorithm in Fig 5 of the paper
is not correct. The set “resultSet” is initialized with the original instances, and then the While loop in the Algorithm run until resultSet is empty, which never holds. Also, the resultSet is only extended in the loop. Our implementation is changed in the following way: we generate twice as many instances are required to balance the dataset, and repeat the loop until the number of new samples added to the training set is enough to balance the dataset.
ProWSyn
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ProWSyn()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
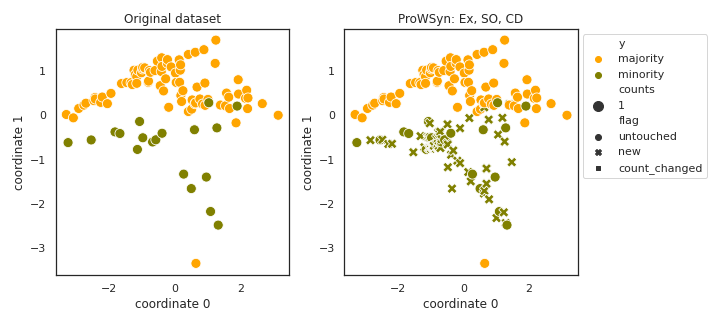
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{prowsyn, author="Barua, Sukarna and Islam, Md. Monirul and Murase, Kazuyuki", editor="Pei, Jian and Tseng, Vincent S. and Cao, Longbing and Motoda, Hiroshi and Xu, Guandong", title="ProWSyn: Proximity Weighted Synthetic Oversampling Technique for Imbalanced Data Set Learning", booktitle="Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining", year="2013", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="317--328", isbn="978-3-642-37456-2" }
SL_graph_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SL_graph_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
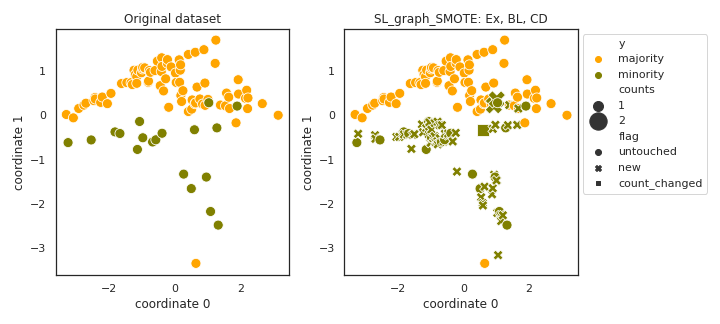
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{sl_graph_smote, author = {Bunkhumpornpat, Chumpol and Subpaiboonkit, Sitthichoke}, booktitle= {13th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies}, year = {2013}, month = {09}, pages = {570-575}, title = {Safe level graph for synthetic minority over-sampling techniques}, isbn = {978-1-4673-5578-0} }
NRSBoundary_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.NRSBoundary_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
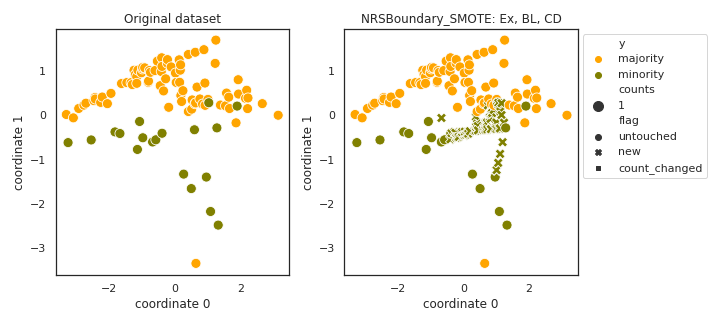
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{nrsboundary_smote, author= {Feng, Hu and Hang, Li}, title= {A Novel Boundary Oversampling Algorithm Based on Neighborhood Rough Set Model: NRSBoundary-SMOTE}, journal= {Mathematical Problems in Engineering}, year= {2013}, pages= {10}, doi= {10.1155/2013/694809}, url= {http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/694809} }
LVQ_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.LVQ_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
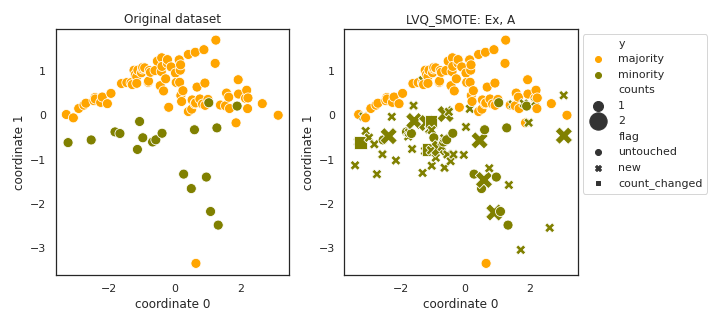
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{lvq_smote, title={LVQ-SMOTE – Learning Vector Quantization based Synthetic Minority Over–sampling Technique for biomedical data}, author={Munehiro Nakamura and Yusuke Kajiwara and Atsushi Otsuka and Haruhiko Kimura}, booktitle={BioData Mining}, year={2013} }
- Notes:
- This implementation is only a rough approximation of the method
described in the paper. The main problem is that the paper uses many datasets to find similar patterns in the codebooks and replicate patterns appearing in other datasets to the imbalanced datasets based on their relative position compared to the codebook elements. What we do is clustering the minority class to extract a codebook as kmeans cluster means, then, find pairs of codebook elements which have the most similar relative position to a randomly selected pair of codebook elements, and translate nearby minority samples from the neighborhood one pair of codebook elements to the neighborood of another pair of codebook elements.
SOI_CJ
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SOI_CJ()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
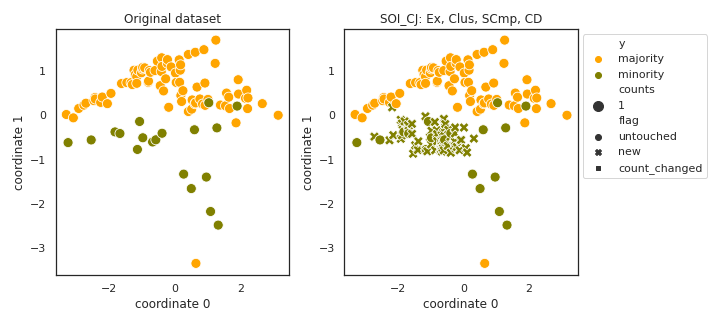
- References:
BibTex:
@article{soi_cj, author = {Sánchez, Atlántida I. and Morales, Eduardo and Gonzalez, Jesus}, year = {2013}, month = {01}, pages = {}, title = {Synthetic Oversampling of Instances Using Clustering}, volume = {22}, booktitle = {International Journal of Artificial Intelligence Tools} }
ROSE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ROSE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
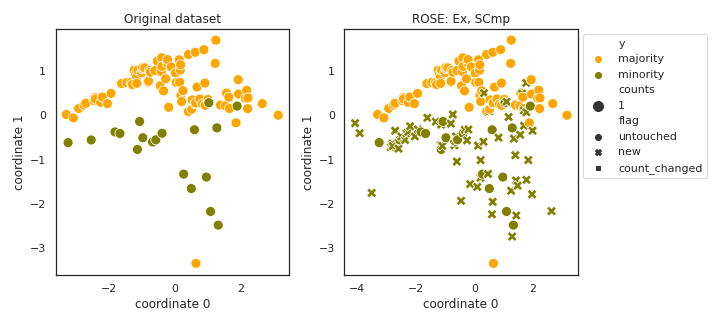
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{rose, author="Menardi, Giovanna and Torelli, Nicola", title="Training and assessing classification rules with imbalanced data", journal="Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery", year="2014", month="Jan", day="01", volume="28", number="1", pages="92--122", issn="1573-756X", doi="10.1007/s10618-012-0295-5", url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-012-0295-5" }
- Notes:
- It is not entirely clear if the authors propose kernel density
estimation or the fitting of simple multivariate Gaussians on the minority samples. The latter seems to be more likely, I implement that approach.
SMOTE_OUT
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_OUT()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
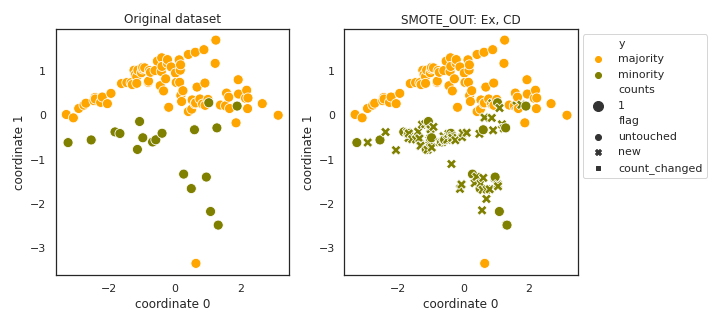
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_out_smote_cosine_selected_smote, title={SMOTE-Out, SMOTE-Cosine, and Selected-SMOTE: An enhancement strategy to handle imbalance in data level}, author={Fajri Koto}, journal={2014 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information System}, year={2014}, pages={280-284} }
SMOTE_Cosine
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_Cosine()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
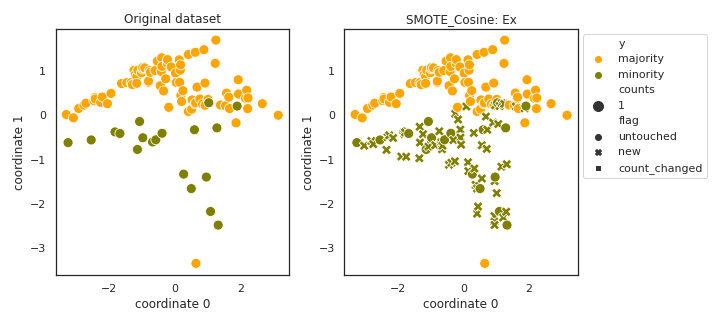
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_out_smote_cosine_selected_smote, title={SMOTE-Out, SMOTE-Cosine, and Selected-SMOTE: An enhancement strategy to handle imbalance in data level}, author={Fajri Koto}, journal={2014 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information System}, year={2014}, pages={280-284} }
Selected_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Selected_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
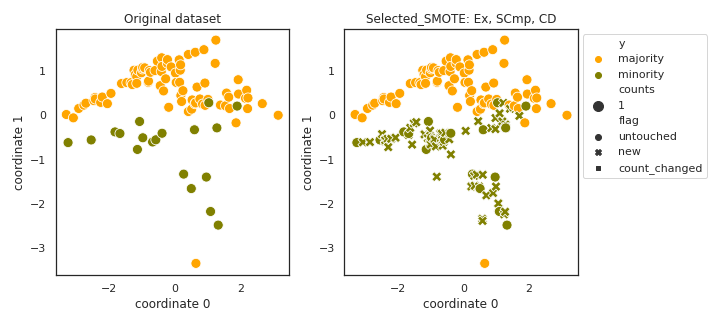
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_out_smote_cosine_selected_smote, title={SMOTE-Out, SMOTE-Cosine, and Selected-SMOTE: An enhancement strategy to handle imbalance in data level}, author={Fajri Koto}, journal={2014 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information System}, year={2014}, pages={280-284} }
- Notes:
- Significant attribute selection was not described in the paper,
therefore we have implemented something meaningful.
LN_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.LN_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
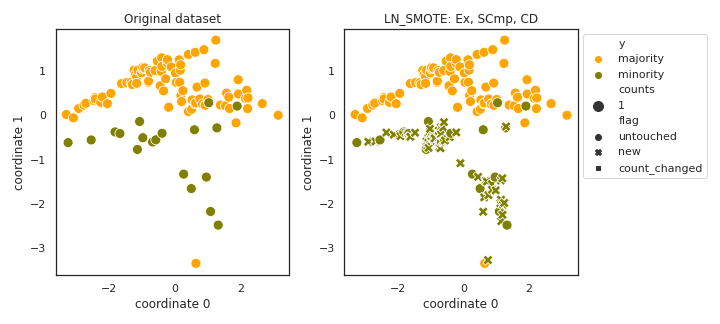
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{ln_smote, author={Maciejewski, T. and Stefanowski, J.}, booktitle={2011 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Data Mining (CIDM)}, title={Local neighbourhood extension of SMOTE for mining imbalanced data}, year={2011}, volume={}, number={}, pages={104-111}, keywords={Bayes methods;data mining;pattern classification;local neighbourhood extension;imbalanced data mining; focused resampling technique;SMOTE over-sampling method;naive Bayes classifiers;Noise measurement;Noise; Decision trees;Breast cancer; Sensitivity;Data mining;Training}, doi={10.1109/CIDM.2011.5949434}, ISSN={}, month={April}}
MWMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.MWMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
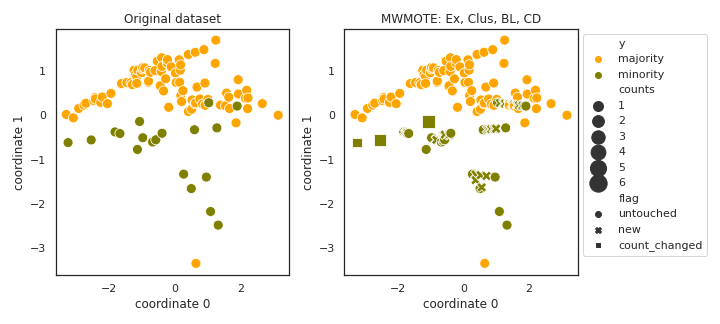
- References:
BibTex:
@ARTICLE{mwmote, author={Barua, S. and Islam, M. M. and Yao, X. and Murase, K.}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering}, title={MWMOTE--Majority Weighted Minority Oversampling Technique for Imbalanced Data Set Learning}, year={2014}, volume={26}, number={2}, pages={405-425}, keywords={learning (artificial intelligence);pattern clustering;sampling methods;AUC;area under curve;ROC;receiver operating curve;G-mean; geometric mean;minority class cluster; clustering approach;weighted informative minority class samples;Euclidean distance; hard-to-learn informative minority class samples;majority class;synthetic minority class samples;synthetic oversampling methods;imbalanced learning problems; imbalanced data set learning; MWMOTE-majority weighted minority oversampling technique;Sampling methods; Noise measurement;Boosting;Simulation; Complexity theory;Interpolation;Abstracts; Imbalanced learning;undersampling; oversampling;synthetic sample generation; clustering}, doi={10.1109/TKDE.2012.232}, ISSN={1041-4347}, month={Feb}}
- Notes:
- The original method was not prepared for the case of having clusters
of 1 elements.
PDFOS
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.PDFOS()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
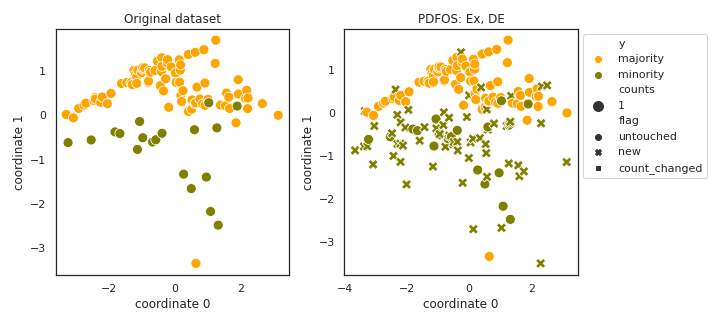
- References:
BibTex:
@article{pdfos, title = "PDFOS: PDF estimation based over-sampling for imbalanced two-class problems", journal = "Neurocomputing", volume = "138", pages = "248 - 259", year = "2014", issn = "0925-2312", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.02.006", author = "Ming Gao and Xia Hong and Sheng Chen and Chris J. Harris and Emad Khalaf", keywords = "Imbalanced classification, Probability density function based over-sampling, Radial basis function classifier, Orthogonal forward selection, Particle swarm optimisation" }
- Notes:
Not prepared for low-rank data.
IPADE_ID
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.IPADE_ID()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
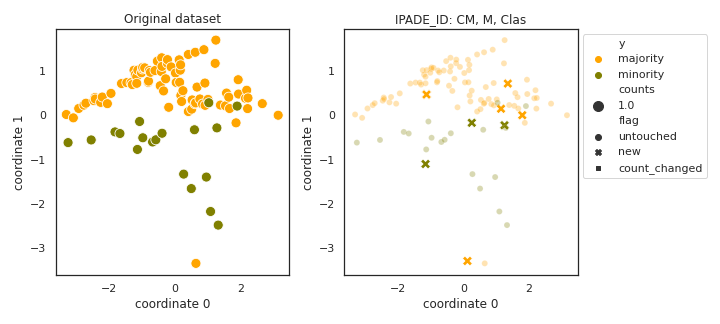
- References:
BibTex:
@article{ipade_id, title = "Addressing imbalanced classification with instance generation techniques: IPADE-ID", journal = "Neurocomputing", volume = "126", pages = "15 - 28", year = "2014", note = "Recent trends in Intelligent Data Analysis Online Data Processing", issn = "0925-2312", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.01.050", author = "Victoria López and Isaac Triguero and Cristóbal J. Carmona and Salvador García and Francisco Herrera", keywords = "Differential evolution, Instance generation, Nearest neighbor, Decision tree, Imbalanced datasets" }
- Notes:
- According to the algorithm, if the addition of a majority sample
doesn’t improve the AUC during the DE optimization process, the addition of no further majority points is tried.
- In the differential evolution the multiplication by a random number
seems have a deteriorating effect, new scaling parameter added to fix this.
It is not specified how to do the evaluation.
RWO_sampling
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.RWO_sampling()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
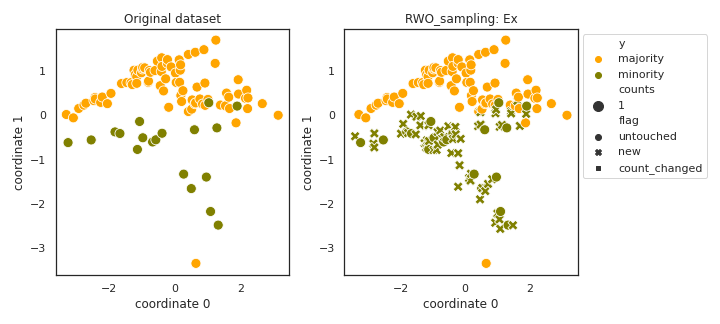
- References:
BibTex:
@article{rwo_sampling, author = {Zhang, Huaxzhang and Li, Mingfang}, year = {2014}, month = {11}, pages = {}, title = {RWO-Sampling: A Random Walk Over-Sampling Approach to Imbalanced Data Classification}, volume = {20}, booktitle = {Information Fusion} }
NEATER
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.NEATER()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
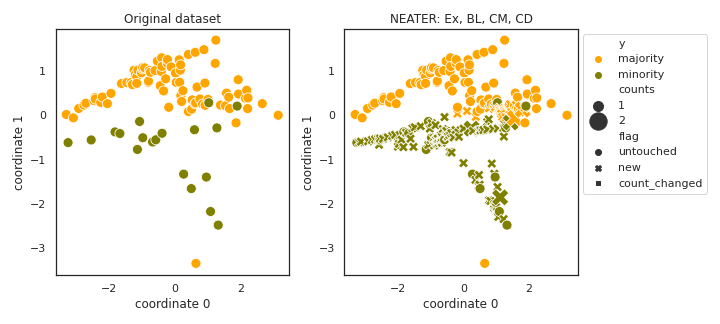
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{neater, author={Almogahed, B. A. and Kakadiaris, I. A.}, booktitle={2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition}, title={NEATER: Filtering of Over-sampled Data Using Non-cooperative Game Theory}, year={2014}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1371-1376}, keywords={data handling;game theory;information filtering;NEATER;imbalanced data problem;synthetic data;filtering of over-sampled data using non-cooperative game theory;Games;Game theory;Vectors; Sociology;Statistics;Silicon; Mathematical model}, doi={10.1109/ICPR.2014.245}, ISSN={1051-4651}, month={Aug}}
- Notes:
- Evolving both majority and minority probabilities as nothing ensures
that the probabilities remain in the range [0,1], and they need to be normalized.
- The inversely weighted function needs to be cut at some value (like
the alpha level), otherwise it will overemphasize the utility of having differing neighbors next to each other.
DEAGO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.DEAGO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
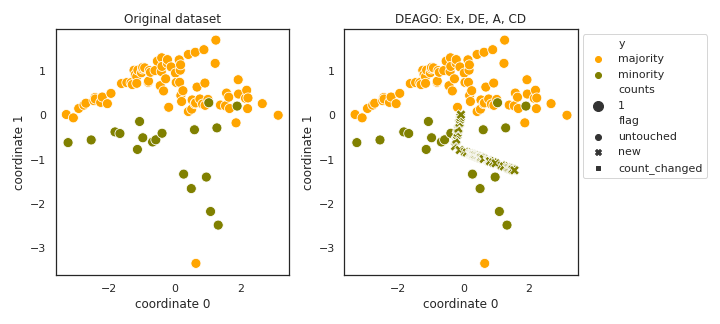
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{deago, author={Bellinger, C. and Japkowicz, N. and Drummond, C.}, booktitle={2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA)}, title={Synthetic Oversampling for Advanced Radioactive Threat Detection}, year={2015}, volume={}, number={}, pages={948-953}, keywords={radioactive waste;advanced radioactive threat detection;gamma-ray spectral classification;industrial nuclear facilities;Health Canadas national monitoring networks;Vancouver 2010; Isotopes;Training;Monitoring; Gamma-rays;Machine learning algorithms; Security;Neural networks;machine learning;classification;class imbalance;synthetic oversampling; artificial neural networks; autoencoders;gamma-ray spectra}, doi={10.1109/ICMLA.2015.58}, ISSN={}, month={Dec}}
- Notes:
There is no hint on the activation functions and amounts of noise.
Gazzah
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Gazzah()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
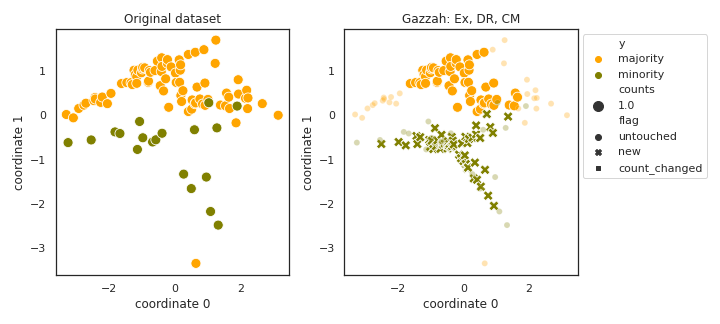
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{gazzah, author={Gazzah, S. and Hechkel, A. and Essoukri Ben Amara, N. }, booktitle={2015 IEEE 12th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals Devices (SSD15)}, title={A hybrid sampling method for imbalanced data}, year={2015}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-6}, keywords={computer vision;image classification; learning (artificial intelligence); sampling methods;hybrid sampling method;imbalanced data; diversification;computer vision domain;classical machine learning systems;intraclass variations; system performances;classification accuracy;imbalanced training data; training data set;over-sampling; minority class;SMOTE star topology; feature vector deletion;intra-class variations;distribution criterion; biometric data;true positive rate; Training data;Principal component analysis;Databases;Support vector machines;Training;Feature extraction; Correlation;Imbalanced data sets; Intra-class variations;Data analysis; Principal component analysis; One-against-all SVM}, doi={10.1109/SSD.2015.7348093}, ISSN={}, month={March}}
MCT
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.MCT()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
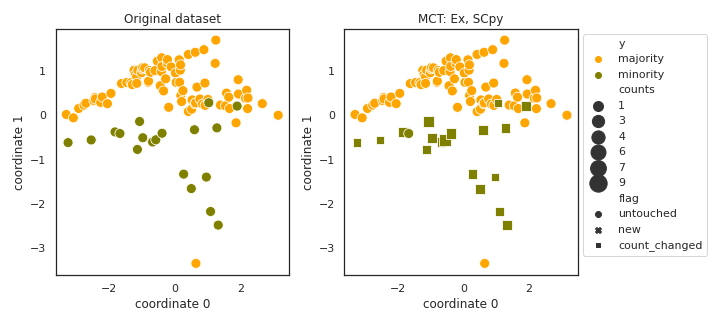
- References:
BibTex:
@article{mct, author = {Jiang, Liangxiao and Qiu, Chen and Li, Chaoqun}, year = {2015}, month = {03}, pages = {1551004}, title = {A Novel Minority Cloning Technique for Cost-Sensitive Learning}, volume = {29}, booktitle = {International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence} }
- Notes:
- Mode is changed to median, distance is changed to Euclidean to
support continuous features, and normalized.
ADG
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ADG()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
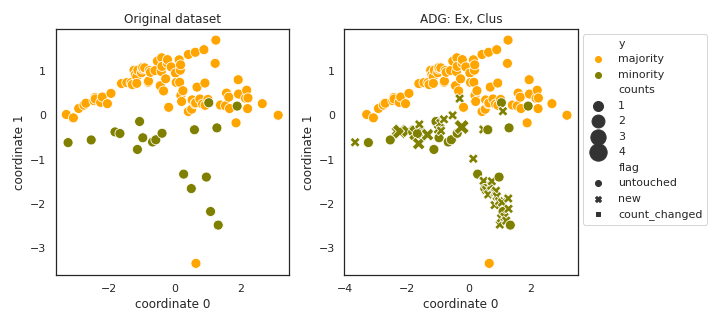
- References:
BibTex:
@article{adg, author = {Pourhabib, A. and Mallick, Bani K. and Ding, Yu}, year = {2015}, month = {16}, pages = {2695--2724}, title = {A Novel Minority Cloning Technique for Cost-Sensitive Learning}, volume = {16}, journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research} }
- Notes:
- This method has a lot of parameters, it becomes fairly hard to
cross-validate thoroughly.
- Fails if matrix is singular when computing alpha_star, fixed
by PCA.
Singularity might be caused by repeating samples.
- Maintaining the kernel matrix becomes unfeasible above a couple
of thousand vectors.
SMOTE_IPF
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_IPF()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
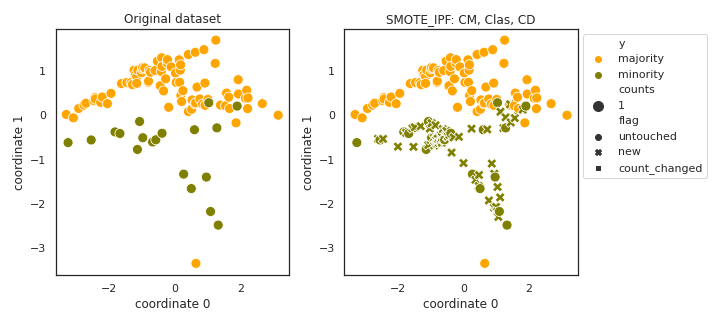
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_ipf, title = "SMOTE–IPF: Addressing the noisy and borderline examples problem in imbalanced classification by a re-sampling method with filtering", journal = "Information Sciences", volume = "291", pages = "184 - 203", year = "2015", issn = "0020-0255", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.051", author = "José A. Sáez and Julián Luengo and Jerzy Stefanowski and Francisco Herrera", keywords = "Imbalanced classification, Borderline examples, Noisy data, Noise filters, SMOTE" }
KernelADASYN
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.KernelADASYN()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
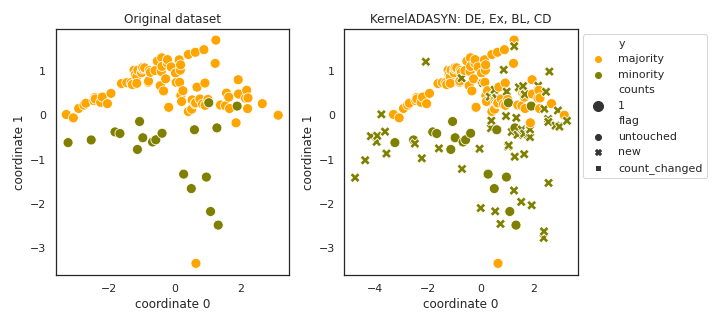
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{kernel_adasyn, author={Tang, B. and He, H.}, booktitle={2015 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC)}, title={KernelADASYN: Kernel based adaptive synthetic data generation for imbalanced learning}, year={2015}, volume={}, number={}, pages={664-671}, keywords={learning (artificial intelligence); pattern classification; sampling methods;KernelADASYN; kernel based adaptive synthetic data generation;imbalanced learning;standard classification algorithms;data distribution; minority class decision rule; expensive minority class data misclassification;kernel based adaptive synthetic over-sampling approach;imbalanced data classification problems;kernel density estimation methods;Kernel; Estimation;Accuracy;Measurement; Standards;Training data;Sampling methods;Imbalanced learning; adaptive over-sampling;kernel density estimation;pattern recognition;medical and healthcare data learning}, doi={10.1109/CEC.2015.7256954}, ISSN={1089-778X}, month={May}}
- Notes:
- The method of sampling was not specified, Markov Chain Monte Carlo
has been implemented.
Not prepared for improperly conditioned covariance matrix.
MOT2LD
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.MOT2LD()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
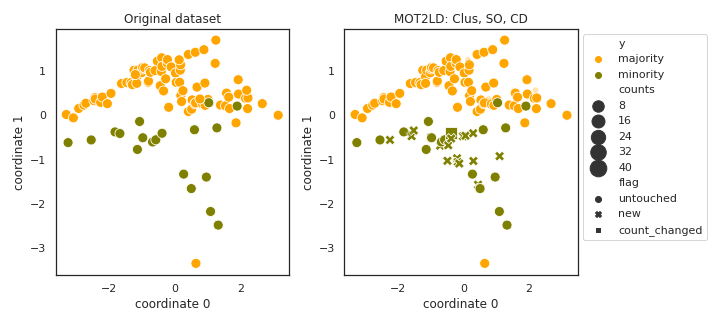
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{mot2ld, author="Xie, Zhipeng and Jiang, Liyang and Ye, Tengju and Li, Xiaoli", editor="Renz, Matthias and Shahabi, Cyrus and Zhou, Xiaofang and Cheema, Muhammad Aamir", title="A Synthetic Minority Oversampling Method Based on Local Densities in Low-Dimensional Space for Imbalanced Learning", booktitle="Database Systems for Advanced Applications", year="2015", publisher="Springer International Publishing", address="Cham", pages="3--18", isbn="978-3-319-18123-3" }
- Notes:
- Clusters might contain 1 elements, and all points can be filtered
as noise.
- Clusters might contain 0 elements as well, if all points are filtered
as noise.
The entire clustering can become empty.
- TSNE is very slow when the number of instances is over a couple
of 1000
V_SYNTH
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.V_SYNTH()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
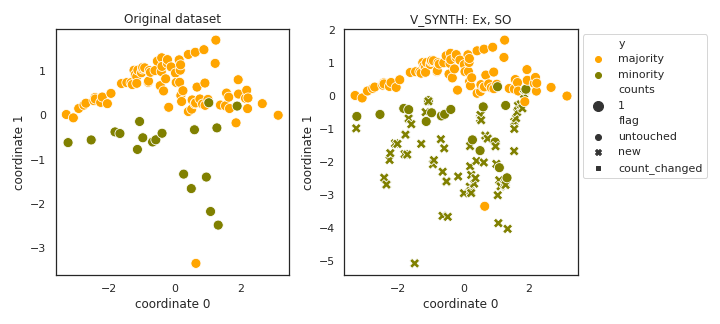
- References:
BibTex:
@article{v_synth, author = {Young,Ii, William A. and Nykl, Scott L. and Weckman, Gary R. and Chelberg, David M.}, title = {Using Voronoi Diagrams to Improve Classification Performances when Modeling Imbalanced Datasets}, journal = {Neural Comput. Appl.}, issue_date = {July 2015}, volume = {26}, number = {5}, month = jul, year = {2015}, issn = {0941-0643}, pages = {1041--1054}, numpages = {14}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1780-0}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-014-1780-0}, acmid = {2790665}, publisher = {Springer-Verlag}, address = {London, UK, UK}, keywords = {Data engineering, Data mining, Imbalanced datasets, Knowledge extraction, Numerical algorithms, Synthetic over-sampling}, }
- Notes:
The proposed encompassing bounding box generation is incorrect.
Voronoi diagram generation in high dimensional spaces is instable
OUPS
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.OUPS()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
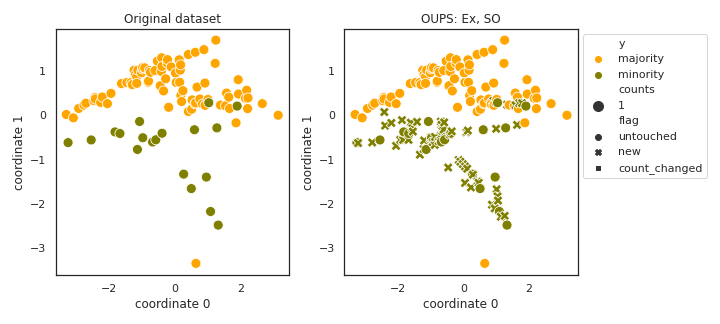
- References:
BibTex:
@article{oups, title = "A priori synthetic over-sampling methods for increasing classification sensitivity in imbalanced data sets", journal = "Expert Systems with Applications", volume = "66", pages = "124 - 135", year = "2016", issn = "0957-4174", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.09.010", author = "William A. Rivera and Petros Xanthopoulos", keywords = "SMOTE, OUPS, Class imbalance, Classification" }
- Notes:
- In the description of the algorithm a fractional number p (j) is
used to index a vector.
SMOTE_D
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_D()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
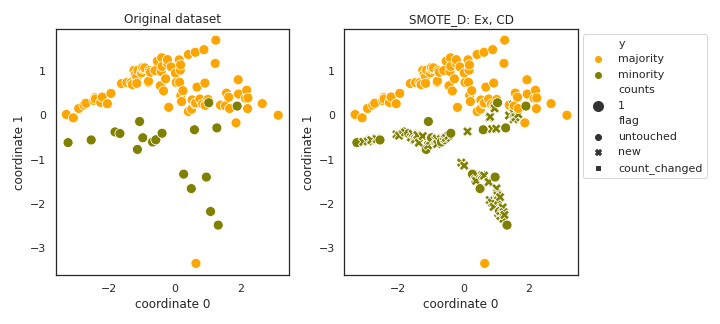
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{smote_d, author="Torres, Fredy Rodr{'i}guez and Carrasco-Ochoa, Jes{'u}s A. and Mart{'i}nez-Trinidad, Jos{'e} Fco.", editor="Mart{'i}nez-Trinidad, Jos{'e} Francisco and Carrasco-Ochoa, Jes{'u}s Ariel and Ayala Ramirez, Victor and Olvera-L{'o}pez, Jos{'e} Arturo and Jiang, Xiaoyi", title="SMOTE-D a Deterministic Version of SMOTE", booktitle="Pattern Recognition", year="2016", publisher="Springer International Publishing", address="Cham", pages="177--188", isbn="978-3-319-39393-3" }
- Notes:
Copying happens if two points are the neighbors of each other.
SMOTE_PSO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_PSO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
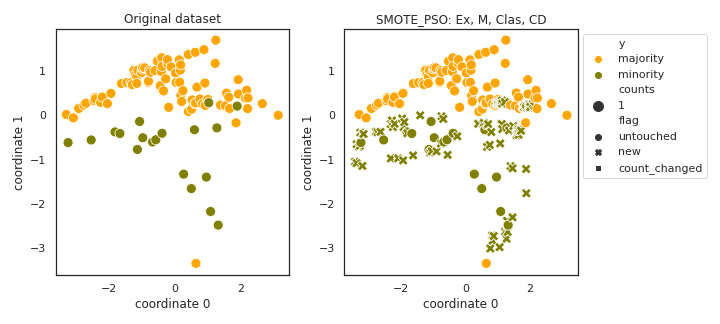
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_pso, title = "PSO-based method for SVM classification on skewed data sets", journal = "Neurocomputing", volume = "228", pages = "187 - 197", year = "2017", note = "Advanced Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications", issn = "0925-2312", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.10.041", author = "Jair Cervantes and Farid Garcia-Lamont and Lisbeth Rodriguez and Asdrúbal López and José Ruiz Castilla and Adrian Trueba", keywords = "Skew data sets, SVM, Hybrid algorithms" }
- Notes:
- I find the description of the technique a bit confusing, especially
on the bounds of the search space of velocities and positions. Equations 15 and 16 specify the lower and upper bounds, the lower bound is in fact a vector while the upper bound is a distance. I tried to implement something meaningful.
- I also find the setting of accelerating constant 2.0 strange, most
of the time the velocity will be bounded due to this choice.
- Also, training and predicting probabilities with a non-linear
SVM as the evaluation function becomes fairly expensive when the number of training vectors reaches a couple of thousands. To reduce computational burden, minority and majority vectors far from the other class are removed to reduce the size of both classes to a maximum of 500 samples. Generally, this shouldn’t really affect the results as the technique focuses on the samples near the class boundaries.
CURE_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.CURE_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
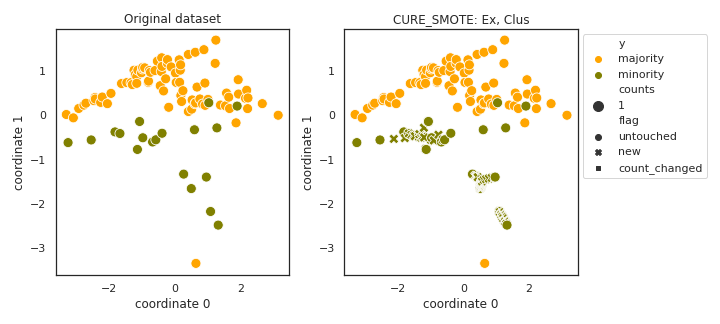
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{cure_smote, author="Ma, Li and Fan, Suohai", title="CURE-SMOTE algorithm and hybrid algorithm for feature selection and parameter optimization based on random forests", journal="BMC Bioinformatics", year="2017", month="Mar", day="14", volume="18", number="1", pages="169", issn="1471-2105", doi="10.1186/s12859-017-1578-z", url="https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1578-z" }
- Notes:
- It is not specified how to determine the cluster with the
“slowest growth rate”
All clusters can be removed as noise.
SOMO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SOMO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
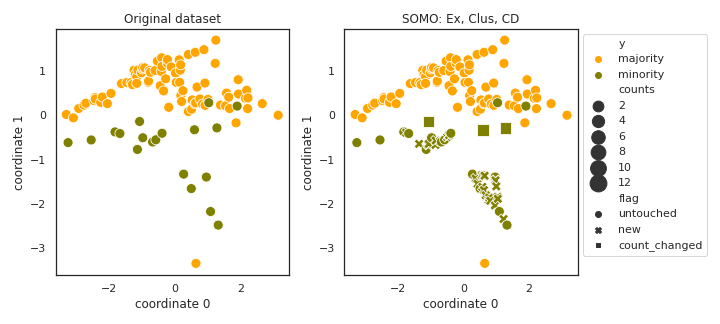
- References:
BibTex:
@article{somo, title = "Self-Organizing Map Oversampling (SOMO) for imbalanced data set learning", journal = "Expert Systems with Applications", volume = "82", pages = "40 - 52", year = "2017", issn = "0957-4174", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.03.073", author = "Georgios Douzas and Fernando Bacao" }
- Notes:
- It is not specified how to handle those cases when a cluster contains
1 minority samples, the mean of within-cluster distances is set to 100 in these cases.
CE_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.CE_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
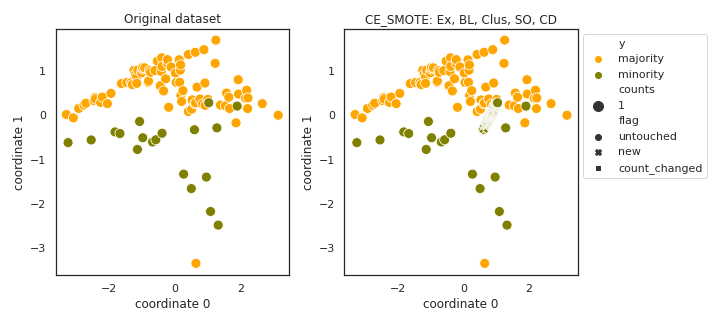
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{ce_smote, author={Chen, S. and Guo, G. and Chen, L.}, booktitle={2010 IEEE 24th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops}, title={A New Over-Sampling Method Based on Cluster Ensembles}, year={2010}, volume={}, number={}, pages={599-604}, keywords={data mining;Internet;pattern classification;pattern clustering; over sampling method;cluster ensembles;classification method; imbalanced data handling;CE-SMOTE; clustering consistency index; cluster boundary minority samples; imbalanced public data set; Mathematics;Computer science; Electronic mail;Accuracy;Nearest neighbor searches;Application software;Data mining;Conferences; Web sites;Information retrieval; classification;imbalanced data sets;cluster ensembles; over-sampling}, doi={10.1109/WAINA.2010.40}, ISSN={}, month={April}}
ISOMAP_Hybrid
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ISOMAP_Hybrid()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
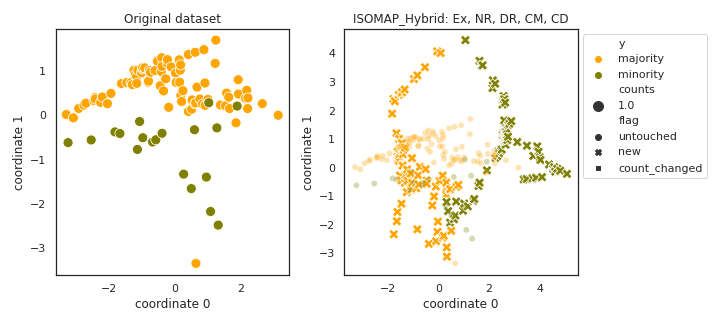
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{isomap_hybrid, author = {Gu, Qiong and Cai, Zhihua and Zhu, Li}, title = {Classification of Imbalanced Data Sets by Using the Hybrid Re-sampling Algorithm Based on Isomap}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Advances in Computation and Intelligence}, series = {ISICA '09}, year = {2009}, isbn = {978-3-642-04842-5}, location = {Huangshi, China}, pages = {287--296}, numpages = {10}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-04843-2_31}, acmid = {1691478}, publisher = {Springer-Verlag}, address = {Berlin, Heidelberg}, keywords = {Imbalanced data set, Isomap, NCR, Smote, re-sampling}, }
Edge_Det_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Edge_Det_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
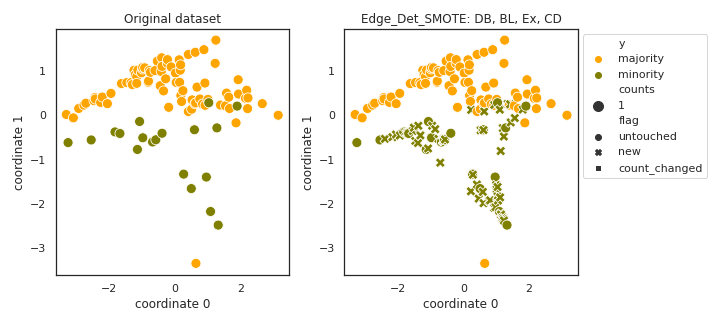
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{Edge_Det_SMOTE, author={Kang, Y. and Won, S.}, booktitle={ICCAS 2010}, title={Weight decision algorithm for oversampling technique on class-imbalanced learning}, year={2010}, volume={}, number={}, pages={182-186}, keywords={edge detection;learning (artificial intelligence);weight decision algorithm;oversampling technique; class-imbalanced learning;class imbalanced data problem;edge detection algorithm;spatial space representation;Classification algorithms;Image edge detection; Training;Noise measurement;Glass; Training data;Machine learning; Imbalanced learning;Classification; Weight decision;Oversampling; Edge detection}, doi={10.1109/ICCAS.2010.5669889}, ISSN={}, month={Oct}}
- Notes:
This technique is very loosely specified.
CBSO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.CBSO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
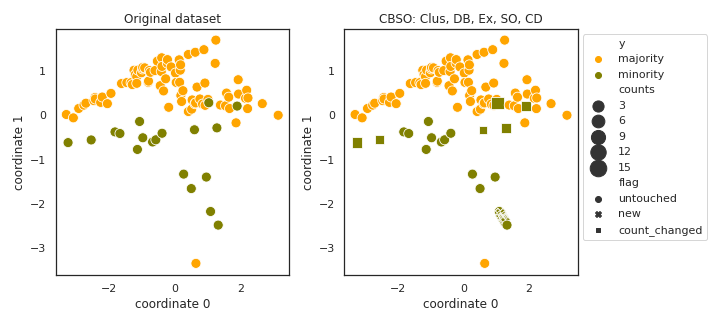
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{cbso, author="Barua, Sukarna and Islam, Md. Monirul and Murase, Kazuyuki", editor="Lu, Bao-Liang and Zhang, Liqing and Kwok, James", title="A Novel Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique for Imbalanced Data Set Learning", booktitle="Neural Information Processing", year="2011", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="735--744", isbn="978-3-642-24958-7" }
- Notes:
Clusters containing 1 element induce cloning of samples.
DBSMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.DBSMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
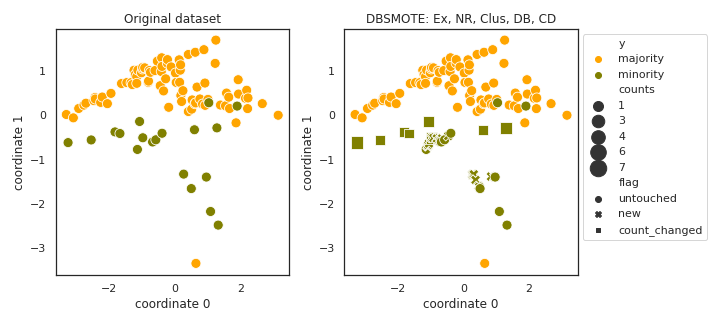
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{dbsmote, author="Bunkhumpornpat, Chumphol and Sinapiromsaran, Krung and Lursinsap, Chidchanok", title="DBSMOTE: Density-Based Synthetic Minority Over-sampling TEchnique", journal="Applied Intelligence", year="2012", month="Apr", day="01", volume="36", number="3", pages="664--684", issn="1573-7497", doi="10.1007/s10489-011-0287-y", url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-011-0287-y" }
- Notes:
Standardization is needed to use absolute eps values.
- The clustering is likely to identify all instances as noise, fixed
by recursive call with increaseing eps.
ASMOBD
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ASMOBD()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
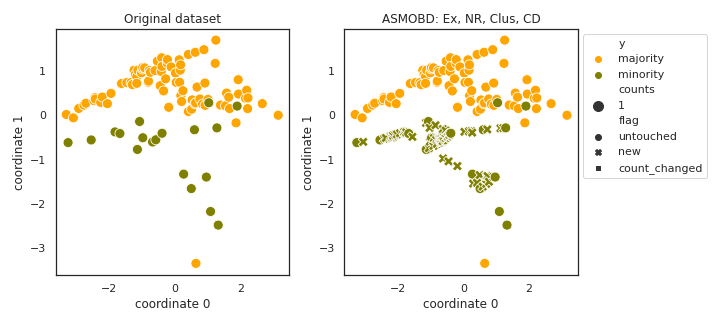
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{asmobd, author={Senzhang Wang and Zhoujun Li and Wenhan Chao and Qinghua Cao}, booktitle={The 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)}, title={Applying adaptive over-sampling technique based on data density and cost-sensitive SVM to imbalanced learning}, year={2012}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-8}, doi={10.1109/IJCNN.2012.6252696}, ISSN={2161-4407}, month={June}}
- Notes:
In order to use absolute thresholds, the data is standardized.
- The technique has many parameters, not easy to find the right
combination.
Assembled_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Assembled_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
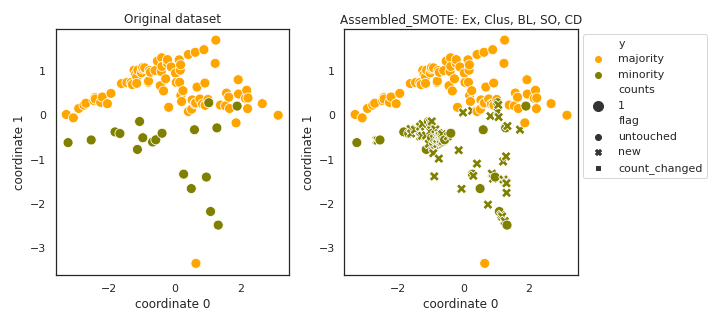
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{assembled_smote, author={Zhou, B. and Yang, C. and Guo, H. and Hu, J.}, booktitle={The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)}, title={A quasi-linear SVM combined with assembled SMOTE for imbalanced data classification}, year={2013}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-7}, keywords={approximation theory;interpolation; pattern classification;sampling methods;support vector machines;trees (mathematics);quasilinear SVM; assembled SMOTE;imbalanced dataset classification problem;oversampling method;quasilinear kernel function; approximate nonlinear separation boundary;mulitlocal linear boundaries; interpolation;data distribution information;minimal spanning tree; local linear partitioning method; linear separation boundary;synthetic minority class samples;oversampled dataset classification;standard SVM; composite quasilinear kernel function; artificial data datasets;benchmark datasets;classification performance improvement;synthetic minority over-sampling technique;Support vector machines;Kernel;Merging;Standards; Sociology;Statistics;Interpolation}, doi={10.1109/IJCNN.2013.6707035}, ISSN={2161-4407}, month={Aug}}
- Notes:
- Absolute value of the angles extracted should be taken.
(implemented this way)
- It is not specified how many samples are generated in the various
clusters.
SDSMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SDSMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
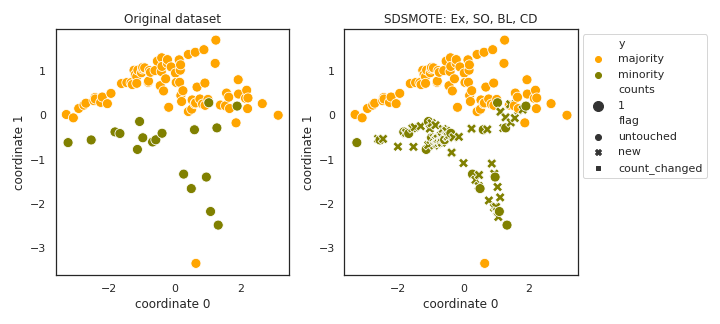
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{sdsmote, author={Li, K. and Zhang, W. and Lu, Q. and Fang, X.}, booktitle={2014 International Conference on Identification, Information and Knowledge in the Internet of Things}, title={An Improved SMOTE Imbalanced Data Classification Method Based on Support Degree}, year={2014}, volume={}, number={}, pages={34-38}, keywords={data mining;pattern classification; sampling methods;improved SMOTE imbalanced data classification method;support degree;data mining; class distribution;imbalanced data-set classification;over sampling method;minority class sample generation;minority class sample selection;minority class boundary sample identification;Classification algorithms;Training;Bagging;Computers; Testing;Algorithm design and analysis; Data mining;Imbalanced data-sets; Classification;Boundary sample;Support degree;SMOTE}, doi={10.1109/IIKI.2014.14}, ISSN={}, month={Oct}}
DSMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.DSMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
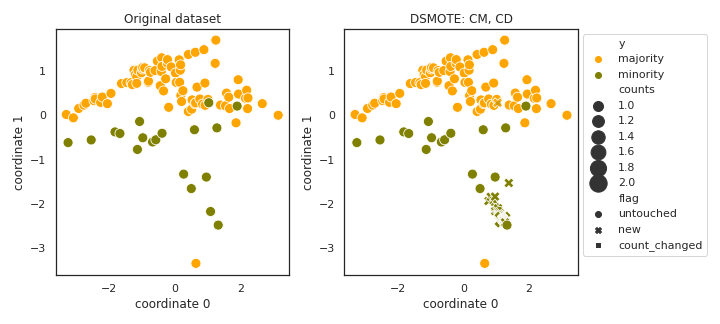
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{dsmote, author={Mahmoudi, S. and Moradi, P. and Akhlaghian, F. and Moradi, R.}, booktitle={2014 4th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE)}, title={Diversity and separable metrics in over-sampling technique for imbalanced data classification}, year={2014}, volume={}, number={}, pages={152-158}, keywords={learning (artificial intelligence); pattern classification;sampling methods;diversity metric;separable metric;over-sampling technique; imbalanced data classification; class distribution techniques; under-sampling technique;DSMOTE method; imbalanced learning problem;diversity measure;separable measure;Iran University of Medical Science;UCI dataset;Accuracy;Classification algorithms;Vectors;Educational institutions;Euclidean distance; Data mining;Diversity measure; Separable Measure;Over-Sampling; Imbalanced Data;Classification problems}, doi={10.1109/ICCKE.2014.6993409}, ISSN={}, month={Oct}}
- Notes:
- The method is highly inefficient when the number of minority samples
is high, time complexity is O(n^3), with 1000 minority samples it takes about 1e9 objective function evaluations to find 1 new sample points. Adding 1000 samples would take about 1e12 evaluations of the objective function, which is unfeasible. We introduce a new parameter, n_step, and during the search for the new sample at most n_step combinations of minority samples are tried.
- Abnormality of minority points is defined in the paper as
D_maj/D_min, high abnormality means that the minority point is close to other minority points and very far from majority points. This is definitely not abnormality, I have implemented the opposite.
- Nothing ensures that the fisher statistics and the variance from
the geometric mean remain comparable, which might skew the optimization towards one of the sub-objectives.
- MinMax normalization doesn’t work, each attribute will have a 0
value, which will make the geometric mean of all attribute 0.
G_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.G_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
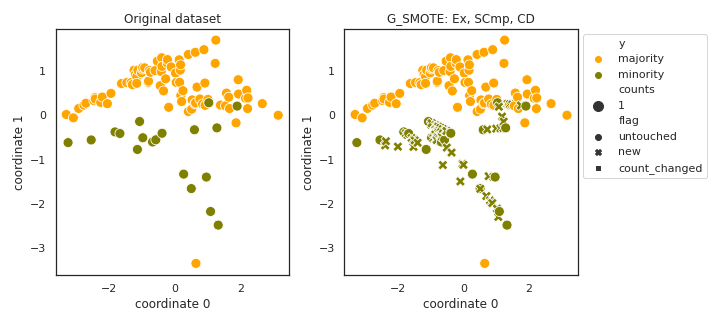
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{g_smote, author={Sandhan, T. and Choi, J. Y.}, booktitle={2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition}, title={Handling Imbalanced Datasets by Partially Guided Hybrid Sampling for Pattern Recognition}, year={2014}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1449-1453}, keywords={Gaussian processes;learning (artificial intelligence);pattern classification; regression analysis;sampling methods; support vector machines;imbalanced datasets;partially guided hybrid sampling;pattern recognition;real-world domains;skewed datasets;dataset rebalancing;learning algorithm; extremely low minority class samples; classification tasks;extracted hidden patterns;support vector machine; logistic regression;nearest neighbor; Gaussian process classifier;Support vector machines;Proteins;Pattern recognition;Kernel;Databases;Gaussian processes;Vectors;Imbalanced dataset; protein classification;ensemble classifier;bootstrapping;Sat-image classification;medical diagnoses}, doi={10.1109/ICPR.2014.258}, ISSN={1051-4651}, month={Aug}}
- Notes:
the non-linear approach is inefficient
NT_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.NT_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
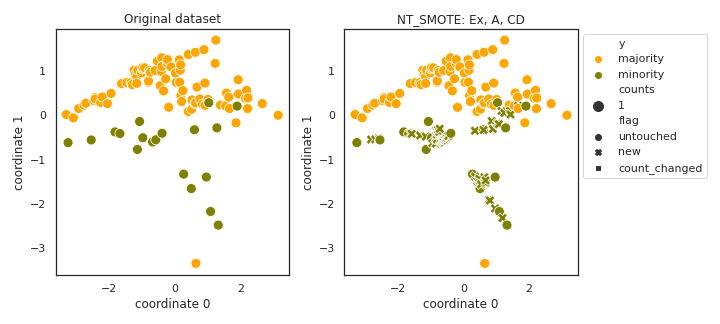
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{nt_smote, author={Xu, Y. H. and Li, H. and Le, L. P. and Tian, X. Y.}, booktitle={2014 Seventh International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization}, title={Neighborhood Triangular Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique for Imbalanced Prediction on Small Samples of Chinese Tourism and Hospitality Firms}, year={2014}, volume={}, number={}, pages={534-538}, keywords={financial management;pattern classification;risk management;sampling methods;travel industry;Chinese tourism; hospitality firms;imbalanced risk prediction;minority class samples; up-sampling approach;neighborhood triangular synthetic minority over-sampling technique;NT-SMOTE; nearest neighbor idea;triangular area sampling idea;single classifiers;data excavation principles;hospitality industry;missing financial indicators; financial data filtering;financial risk prediction;MDA;DT;LSVM;logit;probit; firm risk prediction;Joints; Optimization;imbalanced datasets; NT-SMOTE;neighborhood triangular; random sampling}, doi={10.1109/CSO.2014.104}, ISSN={}, month={July}}
Lee
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Lee()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
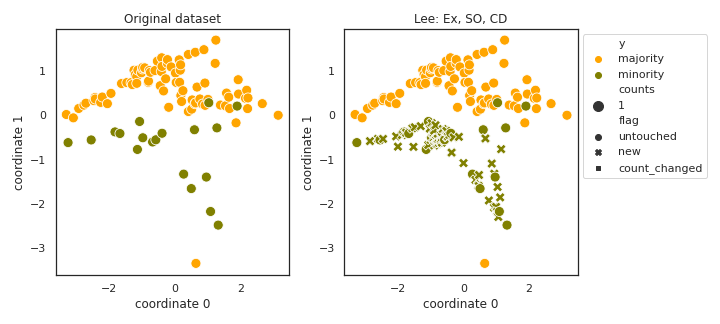
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{lee, author = {Lee, Jaedong and Kim, Noo-ri and Lee, Jee-Hyong}, title = {An Over-sampling Technique with Rejection for Imbalanced Class Learning}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication}, series = {IMCOM '15}, year = {2015}, isbn = {978-1-4503-3377-1}, location = {Bali, Indonesia}, pages = {102:1--102:6}, articleno = {102}, numpages = {6}, doi = {10.1145/2701126.2701181}, acmid = {2701181}, publisher = {ACM}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, keywords = {data distribution, data preprocessing, imbalanced problem, rejection rule, synthetic minority oversampling technique} }
SPY
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SPY()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
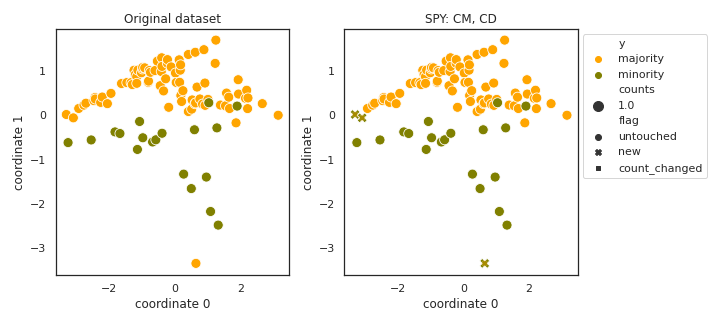
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{spy, author={Dang, X. T. and Tran, D. H. and Hirose, O. and Satou, K.}, booktitle={2015 Seventh International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE)}, title={SPY: A Novel Resampling Method for Improving Classification Performance in Imbalanced Data}, year={2015}, volume={}, number={}, pages={280-285}, keywords={decision making;learning (artificial intelligence);pattern classification; sampling methods;SPY;resampling method;decision-making process; biomedical data classification; class imbalance learning method; SMOTE;oversampling method;UCI machine learning repository;G-mean value;borderline-SMOTE; safe-level-SMOTE;Support vector machines;Training;Bioinformatics; Proteins;Protein engineering;Radio frequency;Sensitivity;Imbalanced dataset;Over-sampling; Under-sampling;SMOTE; borderline-SMOTE}, doi={10.1109/KSE.2015.24}, ISSN={}, month={Oct}}
SMOTE_PSOBAT
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_PSOBAT()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
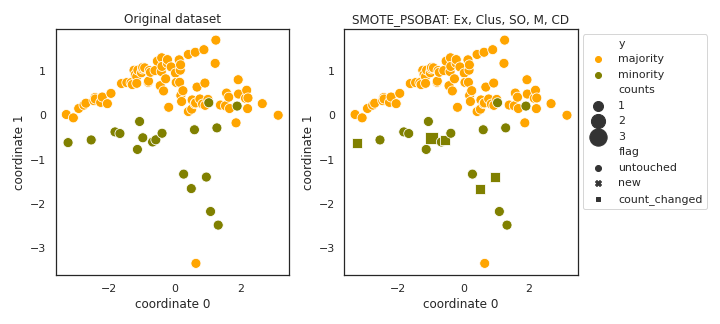
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{smote_psobat, author={Li, J. and Fong, S. and Zhuang, Y.}, booktitle={2015 3rd International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence (ISCBI)}, title={Optimizing SMOTE by Metaheuristics with Neural Network and Decision Tree}, year={2015}, volume={}, number={}, pages={26-32}, keywords={data mining;particle swarm optimisation;pattern classification; data mining;classifier;metaherustics; SMOTE parameters;performance indicators;selection optimization; PSO;particle swarm optimization algorithm;BAT;bat-inspired algorithm; metaheuristic optimization algorithms; nearest neighbors;imbalanced dataset problem;synthetic minority over-sampling technique;decision tree; neural network;Classification algorithms;Neural networks;Decision trees;Training;Optimization;Particle swarm optimization;Data mining;SMOTE; Swarm Intelligence;parameter selection optimization}, doi={10.1109/ISCBI.2015.12}, ISSN={}, month={Dec}}
- Notes:
The parameters of the memetic algorithms are not specified.
- I have checked multiple paper describing the BAT algorithm, but the
meaning of “Generate a new solution by flying randomly” is still unclear.
- It is also unclear if best solutions are recorded for each bat, or
the entire population.
MDO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.MDO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
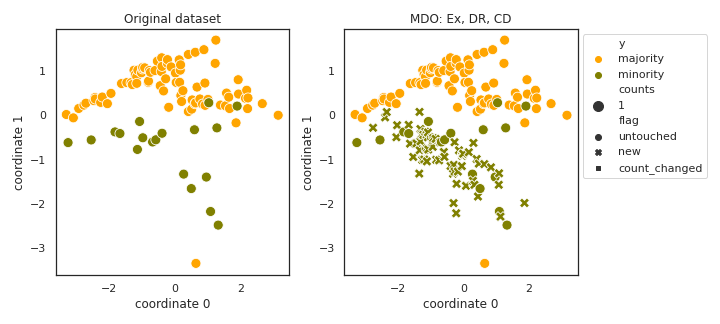
- References:
BibTex:
@ARTICLE{mdo, author={Abdi, L. and Hashemi, S.}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering}, title={To Combat Multi-Class Imbalanced Problems by Means of Over-Sampling Techniques}, year={2016}, volume={28}, number={1}, pages={238-251}, keywords={covariance analysis;learning (artificial intelligence);modelling;pattern classification;sampling methods; statistical distributions;minority class instance modelling;probability contour;covariance structure;MDO; Mahalanobis distance-based oversampling technique;data-oriented technique; model-oriented solution;machine learning algorithm;data skewness;multiclass imbalanced problem;Mathematical model; Training;Accuracy;Eigenvalues and eigenfunctions;Machine learning algorithms;Algorithm design and analysis; Benchmark testing;Multi-class imbalance problems;over-sampling techniques; Mahalanobis distance;Multi-class imbalance problems;over-sampling techniques; Mahalanobis distance}, doi={10.1109/TKDE.2015.2458858}, ISSN={1041-4347}, month={Jan}}
Random_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Random_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{random_smote, author="Dong, Yanjie and Wang, Xuehua", editor="Xiong, Hui and Lee, W. B.", title="A New Over-Sampling Approach: Random-SMOTE for Learning from Imbalanced Data Sets", booktitle="Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management", year="2011", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="343--352", isbn="978-3-642-25975-3" }
ISMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ISMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{ismote, author="Li, Hu and Zou, Peng and Wang, Xiang and Xia, Rongze", editor="Sun, Zengqi and Deng, Zhidong", title="A New Combination Sampling Method for Imbalanced Data", booktitle="Proceedings of 2013 Chinese Intelligent Automation Conference", year="2013", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="547--554", isbn="978-3-642-38466-0" }
VIS_RST
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.VIS_RST()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{vis_rst, author="Borowska, Katarzyna and Stepaniuk, Jaroslaw", editor="Saeed, Khalid and Homenda, Wladyslaw", title="Imbalanced Data Classification: A Novel Re-sampling Approach Combining Versatile Improved SMOTE and Rough Sets", booktitle="Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management", year="2016", publisher="Springer International Publishing", address="Cham", pages="31--42", isbn="978-3-319-45378-1" }
- Notes:
- Replication of DANGER samples will be removed by the last step of
noise filtering.
GASMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.GASMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{gasmote, author="Jiang, Kun and Lu, Jing and Xia, Kuiliang", title="A Novel Algorithm for Imbalance Data Classification Based on Genetic Algorithm Improved SMOTE", journal="Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering", year="2016", month="Aug", day="01", volume="41", number="8", pages="3255--3266", issn="2191-4281", doi="10.1007/s13369-016-2179-2", url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2179-2" }
A_SUWO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.A_SUWO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
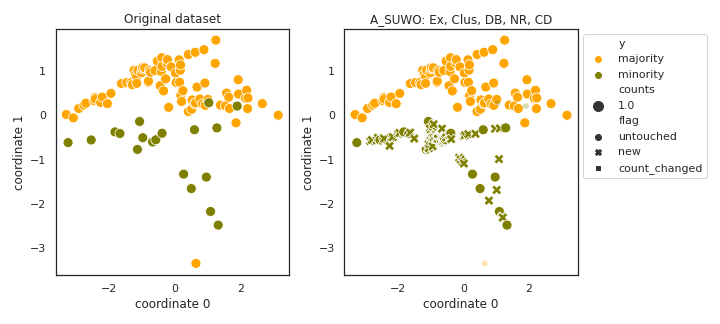
- References:
BibTex:
@article{a_suwo, title = "Adaptive semi-unsupervised weighted oversampling (A-SUWO) for imbalanced datasets", journal = "Expert Systems with Applications", volume = "46", pages = "405 - 416", year = "2016", issn = "0957-4174", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.031", author = "Iman Nekooeimehr and Susana K. Lai-Yuen", keywords = "Imbalanced dataset, Classification, Clustering, Oversampling" }
- Notes:
Equation (7) misses a division by R_j.
It is not specified how to sample from clusters with 1 instances.
SMOTE_FRST_2T
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SMOTE_FRST_2T()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
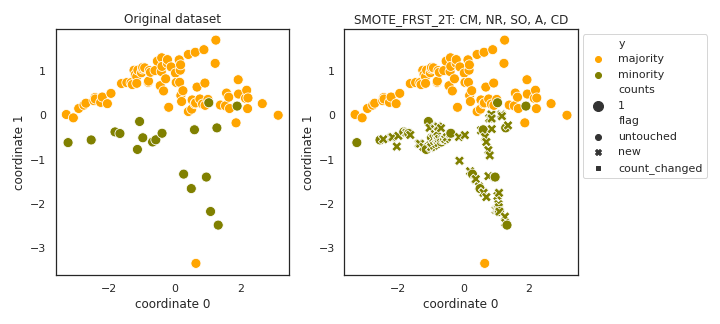
- References:
BibTex:
@article{smote_frst_2t, title = "Fuzzy-rough imbalanced learning for the diagnosis of High Voltage Circuit Breaker maintenance: The SMOTE-FRST-2T algorithm", journal = "Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence", volume = "48", pages = "134 - 139", year = "2016", issn = "0952-1976", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2015.10.009", author = "Ramentol, E. and Gondres, I. and Lajes, S. and Bello, R. and Caballero,Y. and Cornelis, C. and Herrera, F.", keywords = "High Voltage Circuit Breaker (HVCB), Imbalanced learning, Fuzzy rough set theory, Resampling methods" }
- Notes:
- Unlucky setting of parameters might result 0 points added, we have
fixed this by increasing the gamma_S threshold if the number of samples accepted is low.
- Similarly, unlucky setting of parameters might result all majority
samples turned into minority.
- In my opinion, in the algorithm presented in the paper the
relations are incorrect. The authors talk about accepting samples having POS score below a threshold, and in the algorithm in both places POS >= gamma is used.
AND_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.AND_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
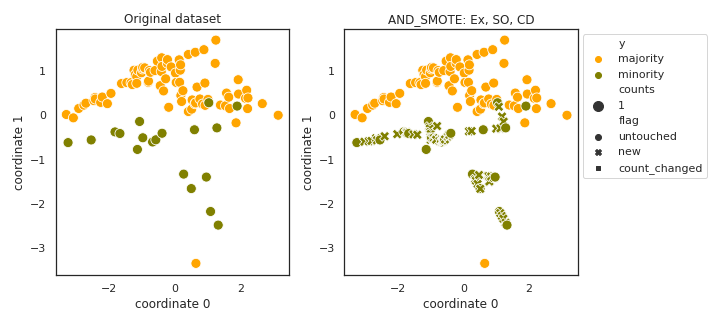
- References:
BibTex:
@inproceedings{and_smote, author = {Yun, Jaesub and Ha, Jihyun and Lee, Jong-Seok}, title = {Automatic Determination of Neighborhood Size in SMOTE}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication}, series = {IMCOM '16}, year = {2016}, isbn = {978-1-4503-4142-4}, location = {Danang, Viet Nam}, pages = {100:1--100:8}, articleno = {100}, numpages = {8}, doi = {10.1145/2857546.2857648}, acmid = {2857648}, publisher = {ACM}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, keywords = {SMOTE, imbalanced learning, synthetic data generation}, }
NRAS
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.NRAS()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
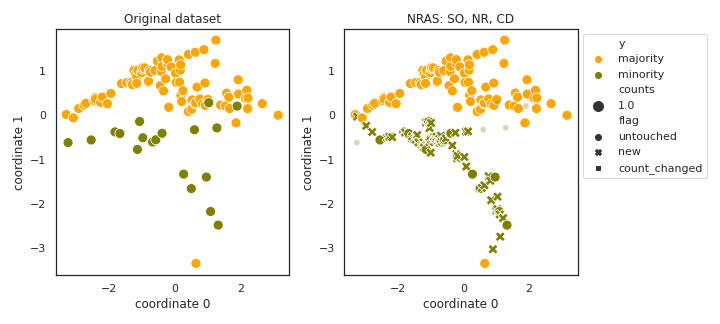
- References:
BibTex:
@article{nras, title = "Noise Reduction A Priori Synthetic Over-Sampling for class imbalanced data sets", journal = "Information Sciences", volume = "408", pages = "146 - 161", year = "2017", issn = "0020-0255", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.04.046", author = "William A. Rivera", keywords = "NRAS, SMOTE, OUPS, Class imbalance, Classification" }
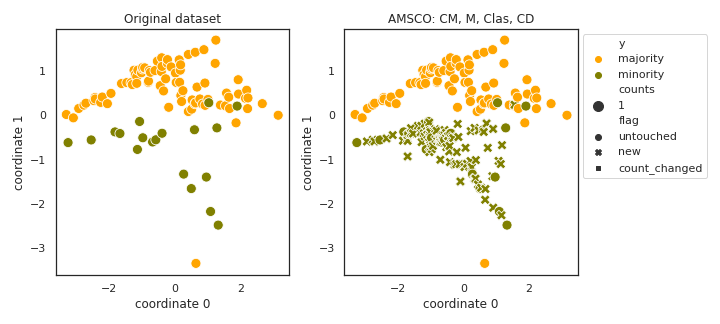
AMSCO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.AMSCO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{amsco, title = "Adaptive multi-objective swarm fusion for imbalanced data classification", journal = "Information Fusion", volume = "39", pages = "1 - 24", year = "2018", issn = "1566-2535", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.03.007", author = "Jinyan Li and Simon Fong and Raymond K. Wong and Victor W. Chu", keywords = "Swarm fusion, Swarm intelligence algorithm, Multi-objective, Crossover rebalancing, Imbalanced data classification" }
- Notes:
- It is not clear how the kappa threshold is used, I do use the RA
score to drive all the evolution. Particularly:
“In the last phase of each iteration, the average Kappa value in current non-inferior set is compare with the latest threshold value, the threshold is then increase further if the average value increases, and vice versa. By doing so, the non-inferior region will be progressively reduced as the Kappa threshold lifts up.”
I don’t see why would the Kappa threshold lift up if the kappa thresholds are decreased if the average Kappa decreases (“vice versa”).
- Due to the interpretation of kappa threshold and the lack of detailed
description of the SIS process, the implementation is not exactly what is described in the paper, but something very similar.
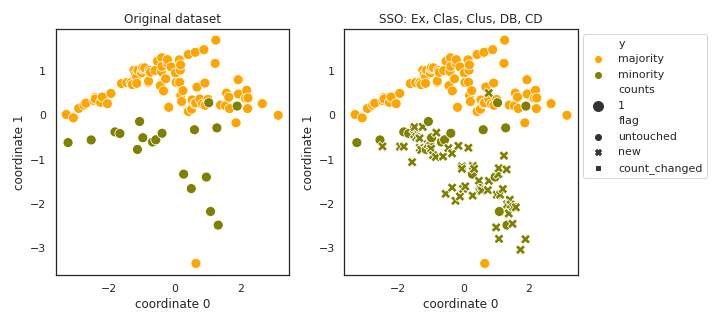
SSO
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SSO()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@InProceedings{sso, author="Rong, Tongwen and Gong, Huachang and Ng, Wing W. Y.", editor="Wang, Xizhao and Pedrycz, Witold and Chan, Patrick and He, Qiang", title="Stochastic Sensitivity Oversampling Technique for Imbalanced Data", booktitle="Machine Learning and Cybernetics", year="2014", publisher="Springer Berlin Heidelberg", address="Berlin, Heidelberg", pages="161--171", isbn="978-3-662-45652-1" }
- Notes:
- In the algorithm step 2d adds a constant to a vector. I have
changed it to a componentwise adjustment, and also used the normalized STSM as I don’t see any reason why it would be some reasonable, bounded value.
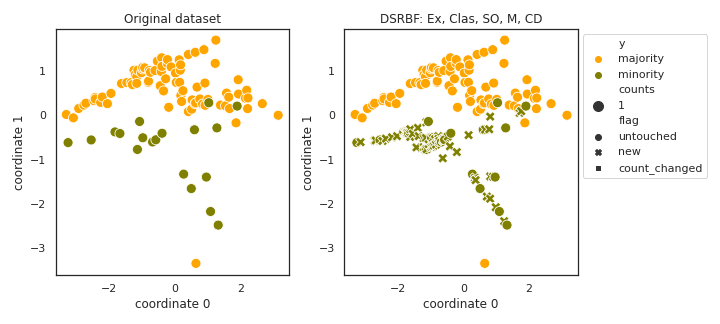
DSRBF
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.DSRBF()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{dsrbf, title = "A dynamic over-sampling procedure based on sensitivity for multi-class problems", journal = "Pattern Recognition", volume = "44", number = "8", pages = "1821 - 1833", year = "2011", issn = "0031-3203", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2011.02.019", author = "Francisco Fernández-Navarro and César Hervás-Martínez and Pedro Antonio Gutiérrez", keywords = "Classification, Multi-class, Sensitivity, Accuracy, Memetic algorithm, Imbalanced datasets, Over-sampling method, SMOTE" }
- Notes:
- It is not entirely clear why J-1 output is supposed where J is the
number of classes.
- The fitness function is changed to a balanced mean loss, as I found
that it just ignores classification on minority samples (class label +1) in the binary case.
The iRprop+ optimization is not implemented.
- The original paper proposes using SMOTE incrementally. Instead of
that, this implementation applies SMOTE to generate all samples needed in the sampling epochs and the evolution of RBF networks is used to select the sampling providing the best results.
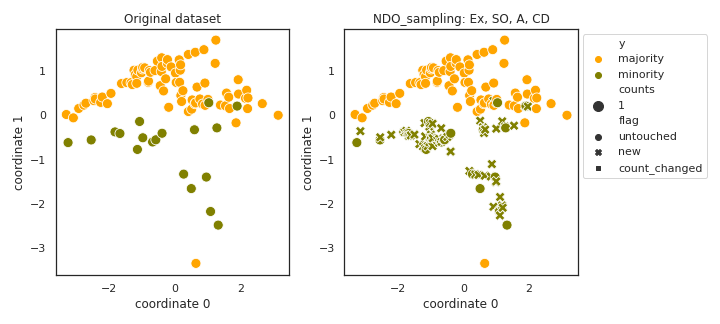
NDO_sampling
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.NDO_sampling()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{ndo_sampling, author={Zhang, L. and Wang, W.}, booktitle={2011 International Conference of Information Technology, Computer Engineering and Management Sciences}, title={A Re-sampling Method for Class Imbalance Learning with Credit Data}, year={2011}, volume={1}, number={}, pages={393-397}, keywords={data handling;sampling methods; resampling method;class imbalance learning;credit rating;imbalance problem;synthetic minority over-sampling technique;sample distribution;synthetic samples; credit data set;Training; Measurement;Support vector machines; Logistics;Testing;Noise;Classification algorithms;class imbalance;credit rating;SMOTE;sample distribution}, doi={10.1109/ICM.2011.34}, ISSN={}, month={Sept}}
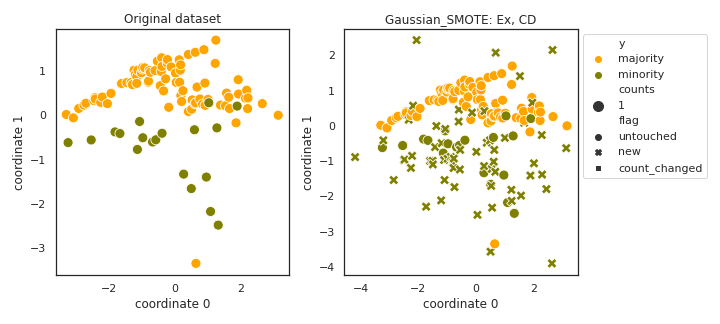
Gaussian_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Gaussian_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{gaussian_smote, title={Gaussian-Based SMOTE Algorithm for Solving Skewed Class Distributions}, author={Hansoo Lee and Jonggeun Kim and Sungshin Kim}, journal={Int. J. Fuzzy Logic and Intelligent Systems}, year={2017}, volume={17}, pages={229-234} }
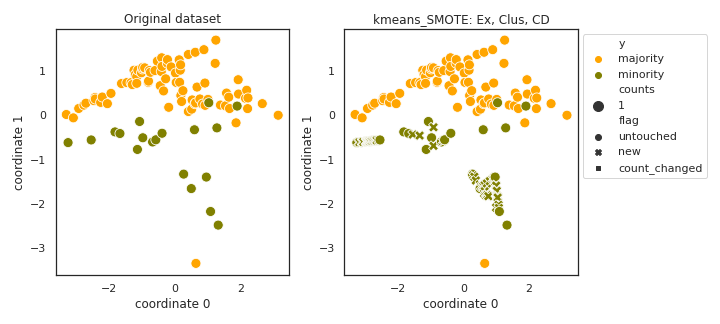
kmeans_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.kmeans_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{kmeans_smote, title = "Improving imbalanced learning through a heuristic oversampling method based on k-means and SMOTE", journal = "Information Sciences", volume = "465", pages = "1 - 20", year = "2018", issn = "0020-0255", doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.06.056", author = "Georgios Douzas and Fernando Bacao and Felix Last", keywords = "Class-imbalanced learning, Oversampling, Classification, Clustering, Supervised learning, Within-class imbalance" }
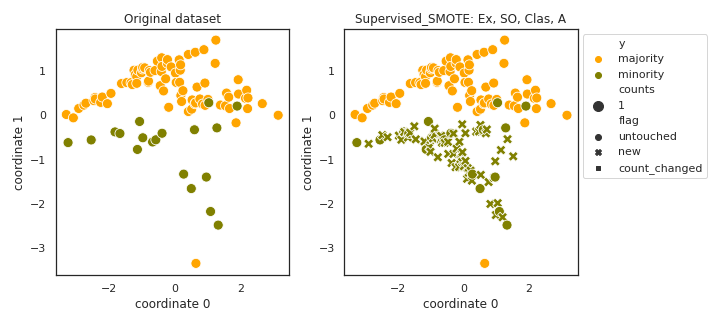
Supervised_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.Supervised_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{supervised_smote, author = {Hu, Jun AND He, Xue AND Yu, Dong-Jun AND Yang, Xi-Bei AND Yang, Jing-Yu AND Shen, Hong-Bin}, journal = {PLOS ONE}, publisher = {Public Library of Science}, title = {A New Supervised Over-Sampling Algorithm with Application to Protein-Nucleotide Binding Residue Prediction}, year = {2014}, month = {09}, volume = {9}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107676}, pages = {1-10}, number = {9}, doi = {10.1371/journal.pone.0107676} }
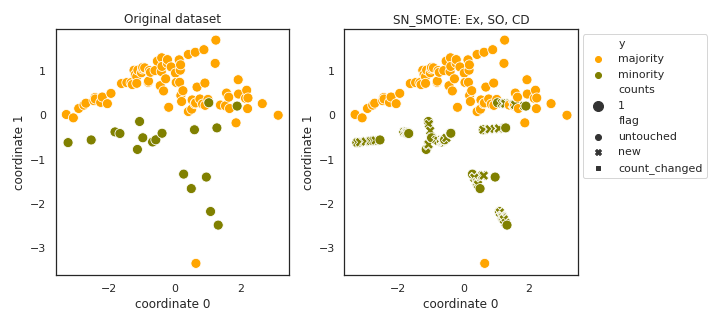
SN_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SN_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@Article{sn_smote, author="Garc{'i}a, V. and S{'a}nchez, J. S. and Mart{'i}n-F{'e}lez, R. and Mollineda, R. A.", title="Surrounding neighborhood-based SMOTE for learning from imbalanced data sets", journal="Progress in Artificial Intelligence", year="2012", month="Dec", day="01", volume="1", number="4", pages="347--362", issn="2192-6360", doi="10.1007/s13748-012-0027-5", url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-012-0027-5" }
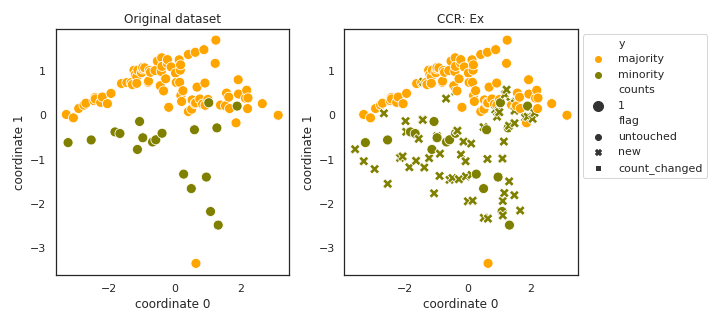
CCR
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.CCR()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{ccr, author = {Koziarski, Michał and Wozniak, Michal}, year = {2017}, month = {12}, pages = {727–736}, title = {CCR: A combined cleaning and resampling algorithm for imbalanced data classification}, volume = {27}, journal = {International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science} }
- Notes:
Adapted from https://github.com/michalkoziarski/CCR
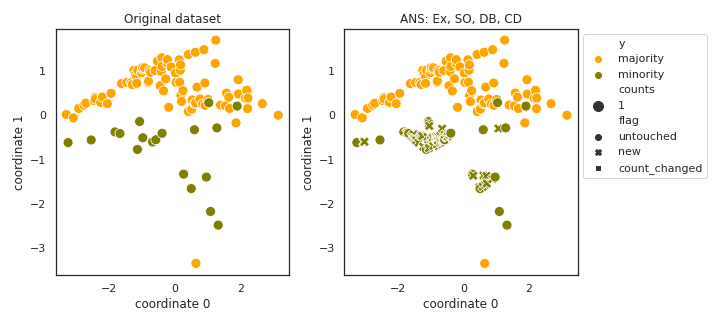
ANS
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ANS()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@article{ans, author = {Siriseriwan, W and Sinapiromsaran, Krung}, year = {2017}, month = {09}, pages = {565-576}, title = {Adaptive neighbor synthetic minority oversampling technique under 1NN outcast handling}, volume = {39}, booktitle = {Songklanakarin Journal of Science and Technology} }
- Notes:
- The method is not prepared for the case when there is no c satisfying
the condition in line 25 of the algorithm, fixed.
The method is not prepared for empty Pused sets, fixed.
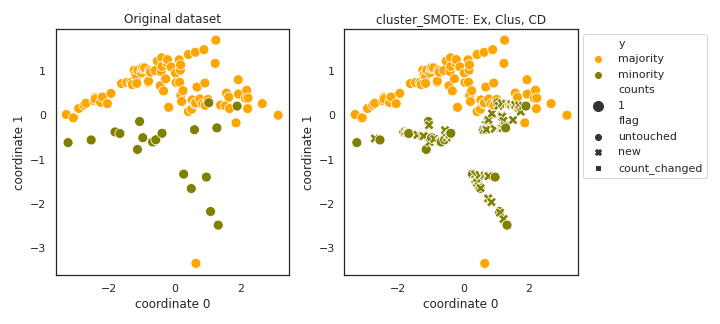
cluster_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.cluster_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{cluster_SMOTE, author={Cieslak, D. A. and Chawla, N. V. and Striegel, A.}, booktitle={2006 IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing}, title={Combating imbalance in network intrusion datasets}, year={2006}, volume={}, number={}, pages={732-737}, keywords={Intelligent networks;Intrusion detection; Telecommunication traffic;Data mining; Computer networks;Data security; Machine learning;Counting circuits; Computer security;Humans}, doi={10.1109/GRC.2006.1635905}, ISSN={}, month={May}}
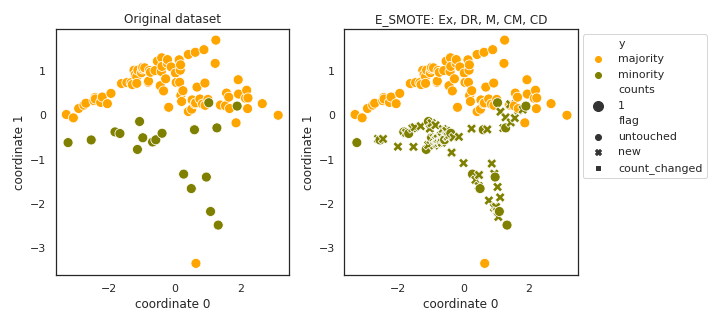
E_SMOTE
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.E_SMOTE()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{e_smote, author={Deepa, T. and Punithavalli, M.}, booktitle={2011 3rd International Conference on Electronics Computer Technology}, title={An E-SMOTE technique for feature selection in High-Dimensional Imbalanced Dataset}, year={2011}, volume={2}, number={}, pages={322-324}, keywords={bioinformatics;data mining;pattern classification;support vector machines; E-SMOTE technique;feature selection; high-dimensional imbalanced dataset; data mining;bio-informatics;dataset balancing;SVM classification;micro array dataset;Feature extraction; Genetic algorithms;Support vector machines;Data mining;Machine learning; Bioinformatics;Cancer;Imbalanced dataset;Featue Selection;E-SMOTE; Support Vector Machine[SVM]}, doi={10.1109/ICECTECH.2011.5941710}, ISSN={}, month={April}}
- Notes:
- This technique is basically unreproducible. I try to implement
something following the idea of applying some simple genetic algorithm for optimization.
- In my best understanding, the technique uses evolutionary algorithms
for feature selection and then applies vanilla SMOTE on the selected features only.
ADOMS
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.ADOMS()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
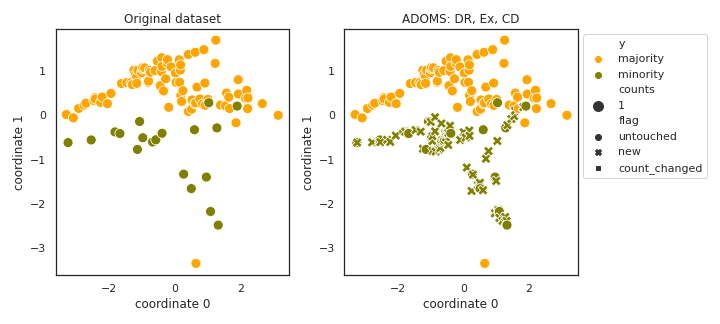
- References:
BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{adoms, author={Tang, S. and Chen, S.}, booktitle={2008 International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine}, title={The generation mechanism of synthetic minority class examples}, year={2008}, volume={}, number={}, pages={444-447}, keywords={medical image processing; generation mechanism;synthetic minority class examples;class imbalance problem;medical image analysis;oversampling algorithm; Principal component analysis; Biomedical imaging;Medical diagnostic imaging;Information technology;Biomedical engineering; Noise generators;Concrete;Nearest neighbor searches;Data analysis; Image analysis}, doi={10.1109/ITAB.2008.4570642}, ISSN={2168-2194}, month={May}}
SYMPROD
API
Example
>>> oversampler= smote_variants.SYMPROD()
>>> X_samp, y_samp= oversampler.sample(X, y)
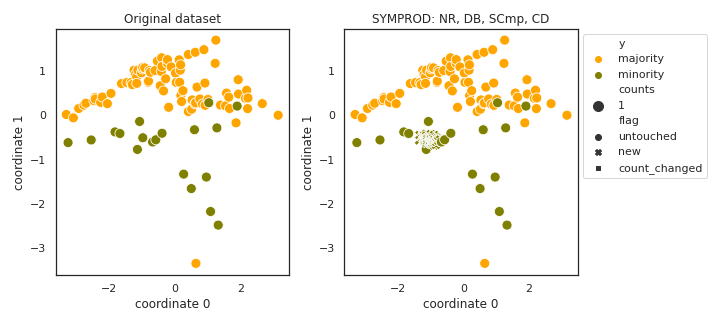
- References:
Bibtex:
@article{kunakorntum2020synthetic, title={A Synthetic Minority Based on Probabilistic Distribution (SyMProD) Oversampling for Imbalanced Datasets}, author={Kunakorntum, Intouch and Hinthong, Woranich and Phunchongharn, Phond}, journal={IEEE Access}, volume={8}, pages={114692--114704}, year={2020}, publisher={IEEE} }